07. 堆排序
07. 堆排序
1. 堆结构
「堆排序(Heap sort)」是一种基于「堆结构」实现的高效排序算法。在介绍「堆排序」之前,我们先来了解一下什么是「堆结构」。
1.1 堆的定义
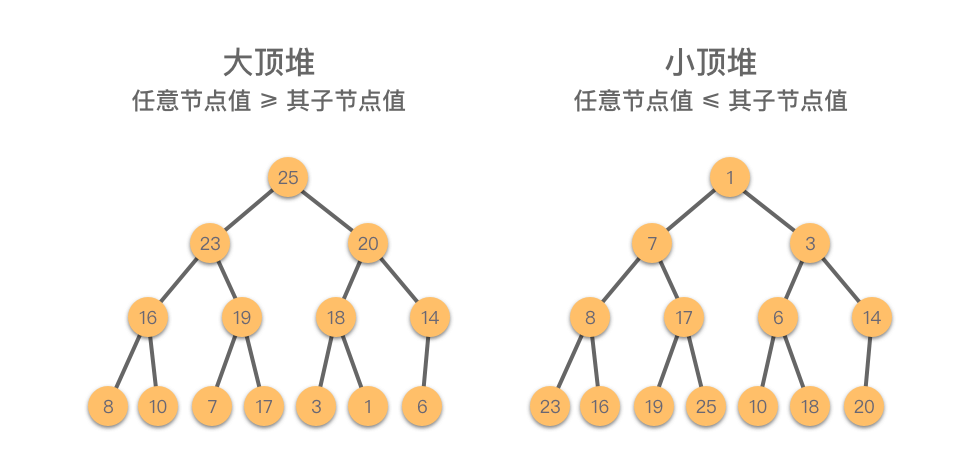
堆(Heap):一种满足以下两个条件之一的完全二叉树:
- 大顶堆(Max Heap):任意节点值 ≥ 其子节点值。
- 小顶堆(Min Heap):任意节点值 ≤ 其子节点值。
1.2 堆的存储结构
堆的逻辑结构就是一颗完全二叉树。如下图所示:
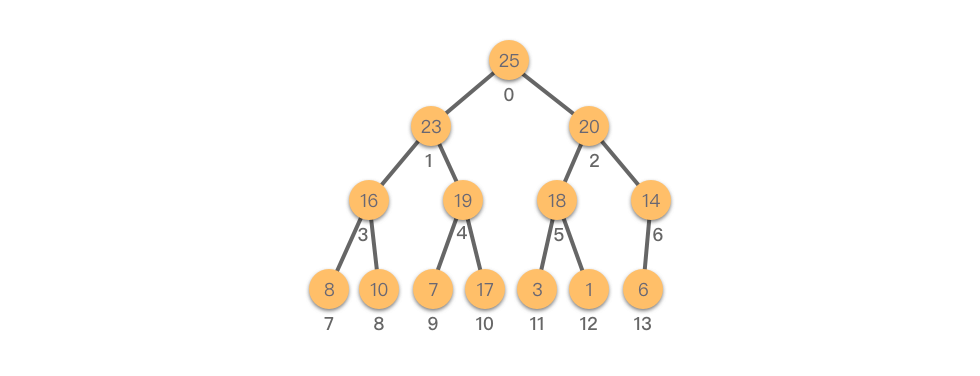
而我们在「07.树 - 01.二叉树 - 01.树与二叉树的基础知识」章节中学过,对于完全二叉树(尤其是满二叉树)来说,采用顺序存储结构(数组)的形式来表示完全二叉树,能够充分利用存储空间。如下图所示:
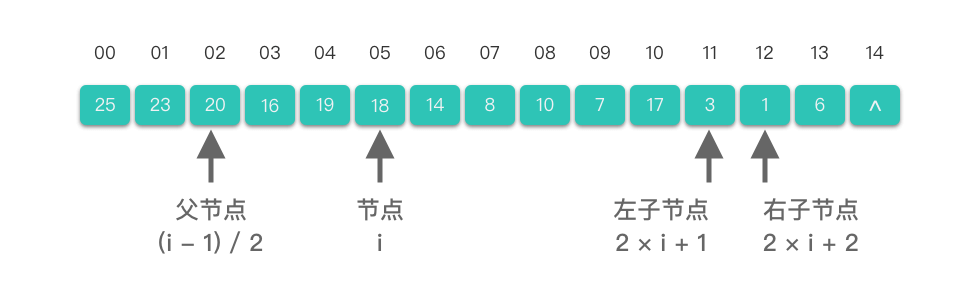
当我们使用顺序存储结构(即数组)来表示堆时,堆中元素的节点编号与数组的索引关系为:
- 如果某二叉树节点(非叶子节点)的下标为
- 如果某二叉树节点(非根结点)的下标为
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.max_heap = []1.3 访问堆顶元素
访问堆顶元素:指的是从堆结构中获取位于堆顶的元素。
在堆中,堆顶元素位于根节点,当我们使用顺序存储结构(即数组)来表示堆时,堆顶元素就是数组的首个元素。
class MaxHeap:
......
def peek(self) -> int:
# 大顶堆为空
if not self.max_heap:
return None
# 返回堆顶元素
return self.max_heap[0]访问堆顶元素不依赖于数组中元素个数,因此时间复杂度为
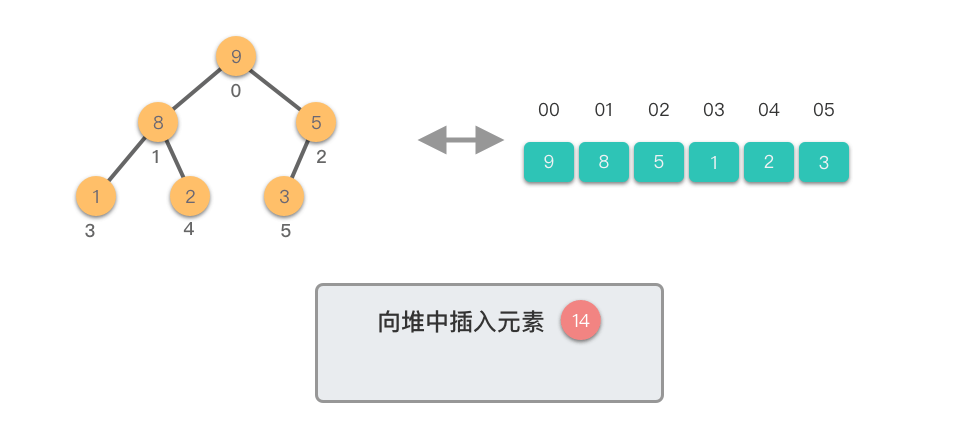
1.4 向堆中插入元素
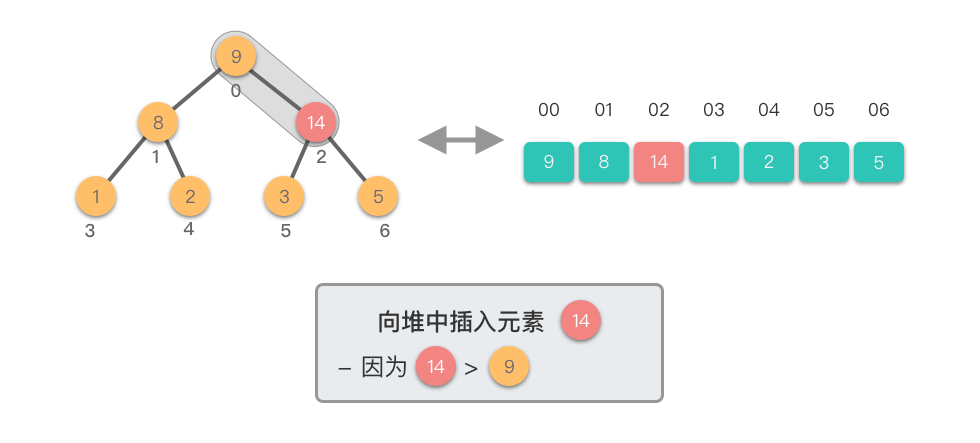
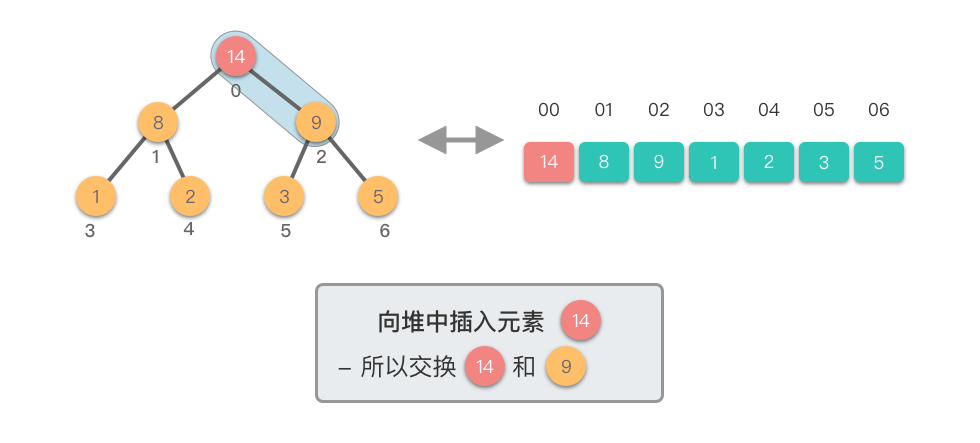
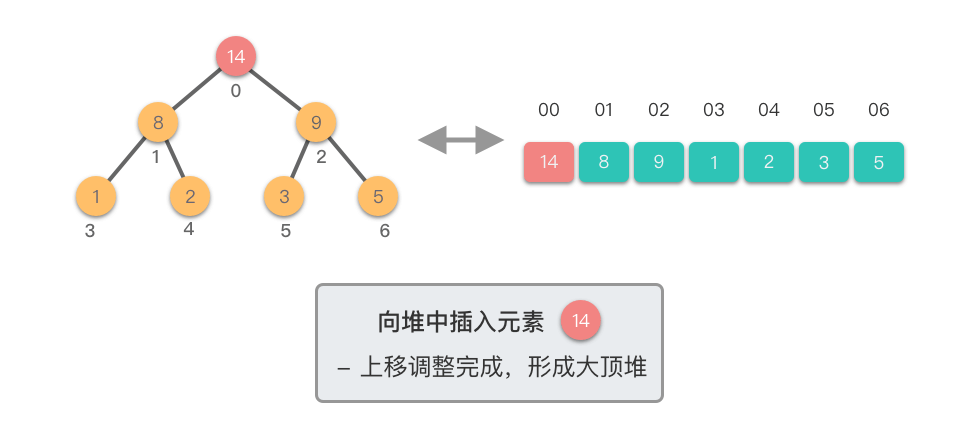
向堆中插入元素:指的将一个新的元素添加到堆中,调整堆结构,以保持堆的特性不变。
向堆中插入元素的步骤如下:
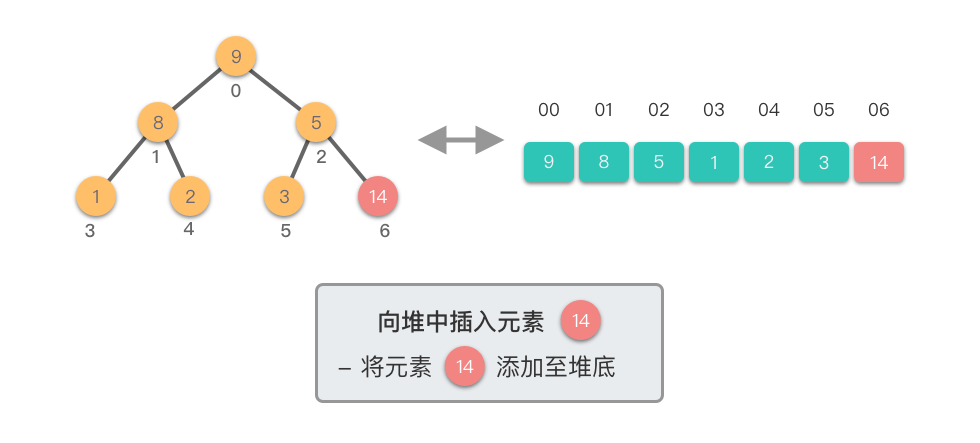
- 将新元素添加到堆的末尾,保持完全二叉树的结构。
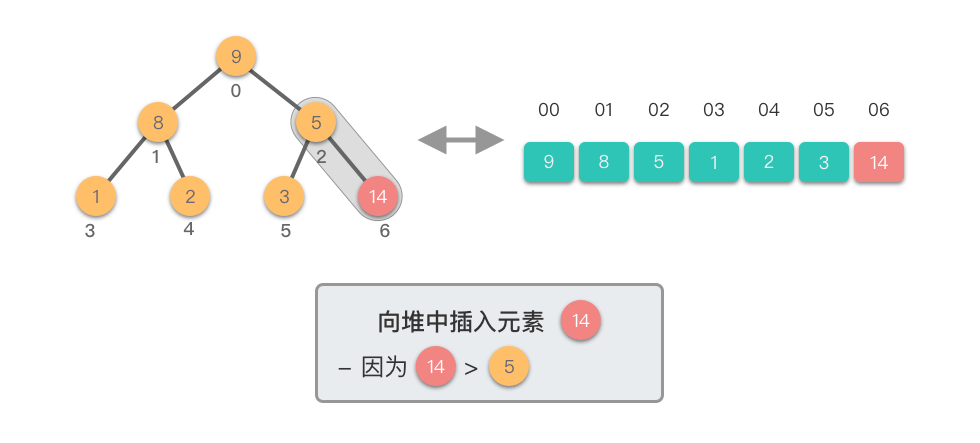
- 从新插入的元素节点开始,将该节点与其父节点进行比较。
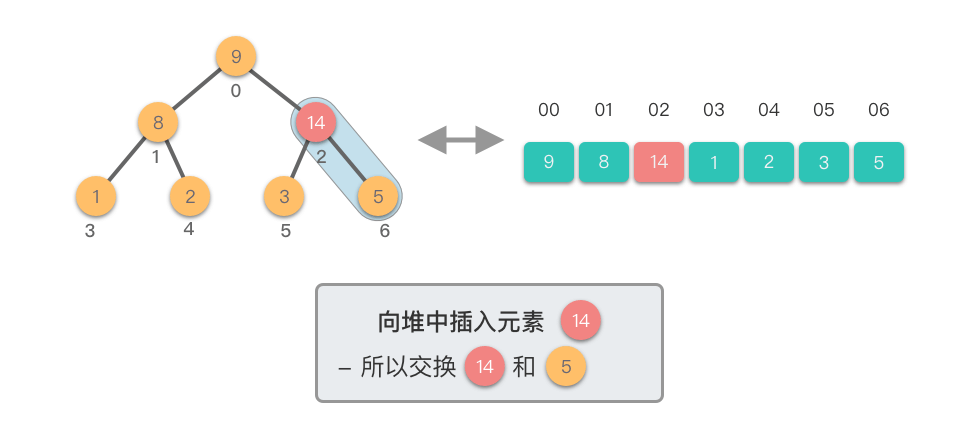
- 如果新节点的值大于其父节点的值,则交换它们,以保持最大堆的特性。
- 如果新节点的值小于等于其父节点的值,说明已满足最大堆的特性,此时结束。
- 重复上述比较和交换步骤,直到新节点不再大于其父节点,或者达到了堆的根节点。
这个过程称为「上移调整(Shift Up)」。因为新插入的元素会逐步向堆的上方移动,直到找到了合适的位置,保持堆的有序性。
::: tabs#heapPush
@tab <1>
@tab <2>
@tab <3>
@tab <4>
@tab <5>
@tab <6>
@tab <7>
:::
class MaxHeap:
......
def push(self, val: int):
# 将新元素添加到堆的末尾
self.max_heap.append(val)
size = len(self.max_heap)
# 从新插入的元素节点开始,进行上移调整
self.__shift_up(size - 1)
def __shift_up(self, i: int):
while (i - 1) // 2 >= 0 and self.max_heap[i] > self.max_heap[(i - 1) // 2]:
self.max_heap[i], self.max_heap[(i - 1) // 2] = self.max_heap[(i - 1) // 2], self.max_heap[i]
i = (i - 1) // 2在最坏情况下,「向堆中插入元素」的时间复杂度为
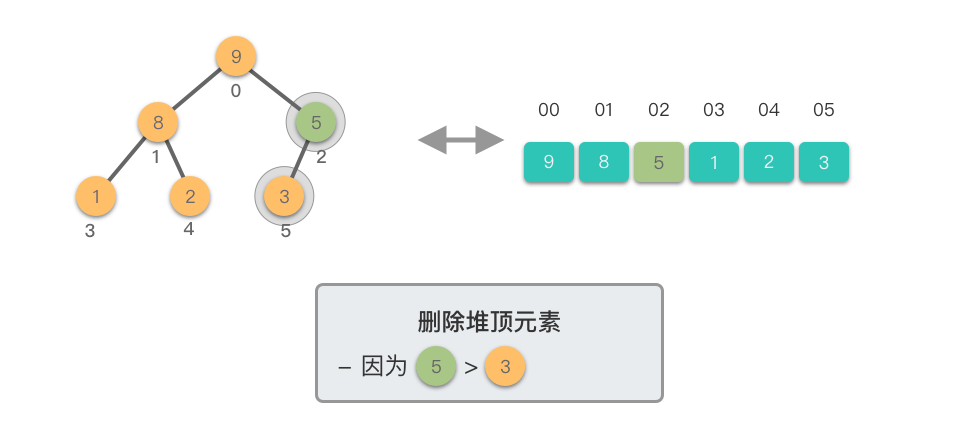
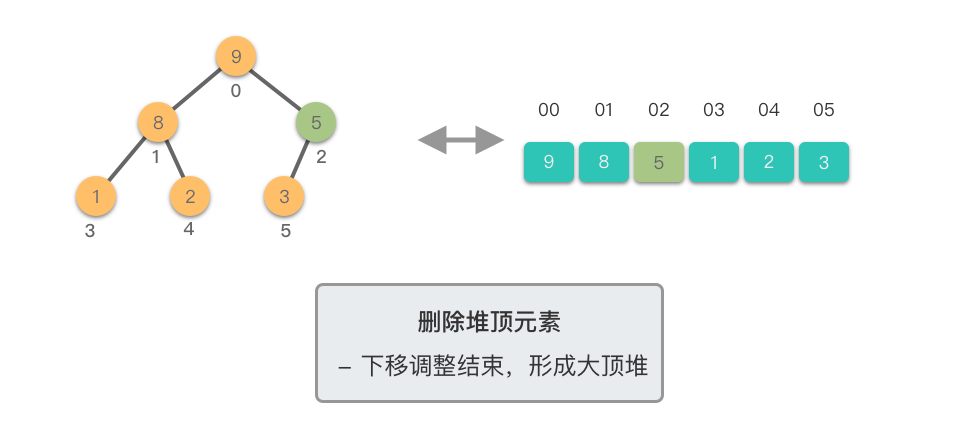
1.5 删除堆顶元素
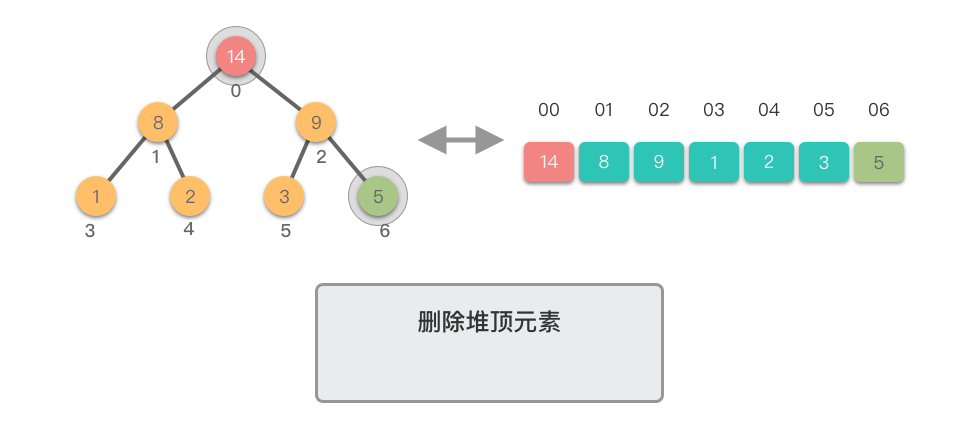
删除堆顶元素:指的是从堆中移除位于堆顶的元素,并重新调整对结果,以保持堆的特性不变。
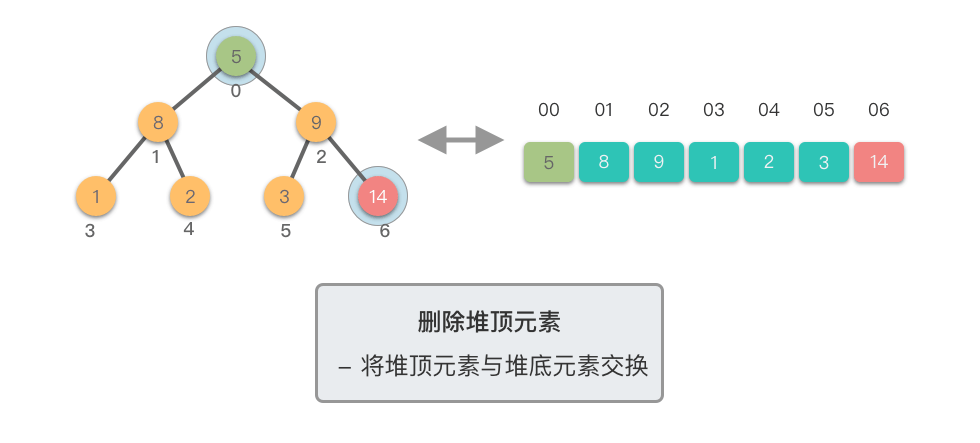
删除堆顶元素的步骤如下:
- 将堆顶元素(即根节点)与堆的末尾元素交换。
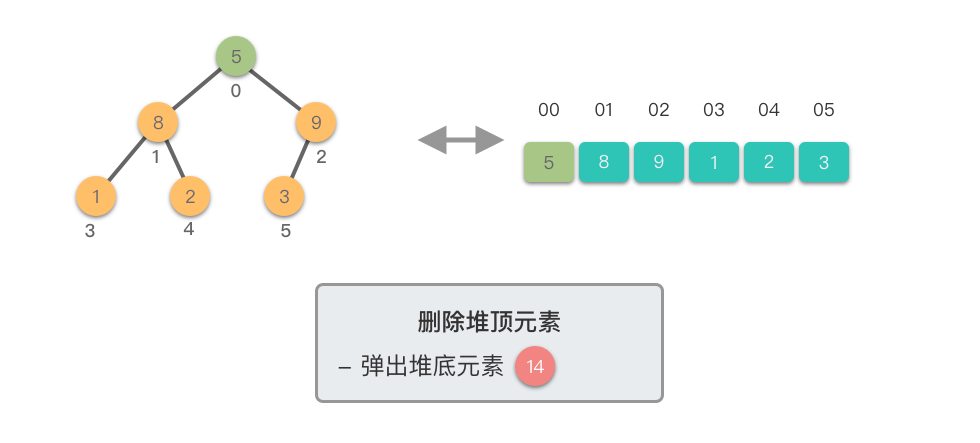
- 移除堆末尾的元素(之前的堆顶),即将其从堆中剔除。
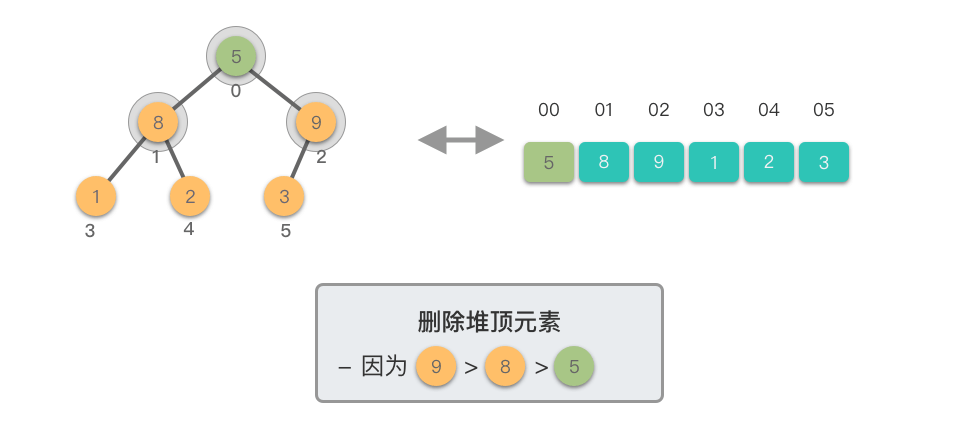
- 从新的堆顶元素开始,将其与其较大的子节点进行比较。
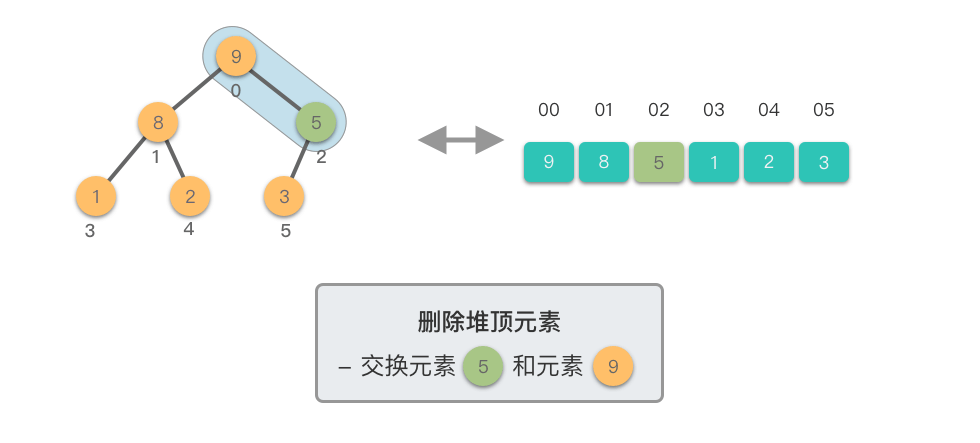
- 如果当前节点的值小于其较大的子节点,则将它们交换。这一步是为了将新的堆顶元素「下沉」到适当的位置,以保持最大堆的特性。
- 如果当前节点的值大于等于其较大的子节点,说明已满足最大堆的特性,此时结束。
- 重复上述比较和交换步骤,直到新的堆顶元素不再小于其子节点,或者达到了堆的底部。
这个过程称为「下移调整(Shift Down)」。因为新的堆顶元素会逐步向堆的下方移动,直到找到了合适的位置,保持堆的有序性。
::: tabs#heapPop
@tab <1>
@tab <2>
@tab <3>
@tab <4>
@tab <5>
@tab <6>
@tab <7>
:::
class MaxHeap:
......
def pop(self) -> int:
# 堆为空
if not self.max_heap:
raise IndexError("堆为空")
size = len(self.max_heap)
self.max_heap[0], self.max_heap[size - 1] = self.max_heap[size - 1], self.max_heap[0]
# 删除堆顶元素
val = self.max_heap.pop()
# 节点数减 1
size -= 1
# 下移调整
self.__shift_down(0, size)
# 返回堆顶元素
return val
def __shift_down(self, i: int, n: int):
while 2 * i + 1 < n:
# 左右子节点编号
left, right = 2 * i + 1, 2 * i + 2
# 找出左右子节点中的较大值节点编号
if 2 * i + 2 >= n:
# 右子节点编号超出范围(只有左子节点
larger = left
else:
# 左子节点、右子节点都存在
if self.max_heap[left] >= self.max_heap[right]:
larger = left
else:
larger = right
# 将当前节点值与其较大的子节点进行比较
if self.max_heap[i] < self.max_heap[larger]:
# 如果当前节点值小于其较大的子节点,则将它们交换
self.max_heap[i], self.max_heap[larger] = self.max_heap[larger], self.max_heap[i]
i = larger
else:
# 如果当前节点值大于等于于其较大的子节点,此时结束
break「删除堆顶元素」的时间复杂度通常为
2. 堆排序
2.1 堆排序算法思想
堆排序(Heap sort)基本思想:
借用「堆结构」所设计的排序算法。将数组转化为大顶堆,重复从大顶堆中取出数值最大的节点,并让剩余的堆结构继续维持大顶堆性质。
2.2 堆排序算法步骤
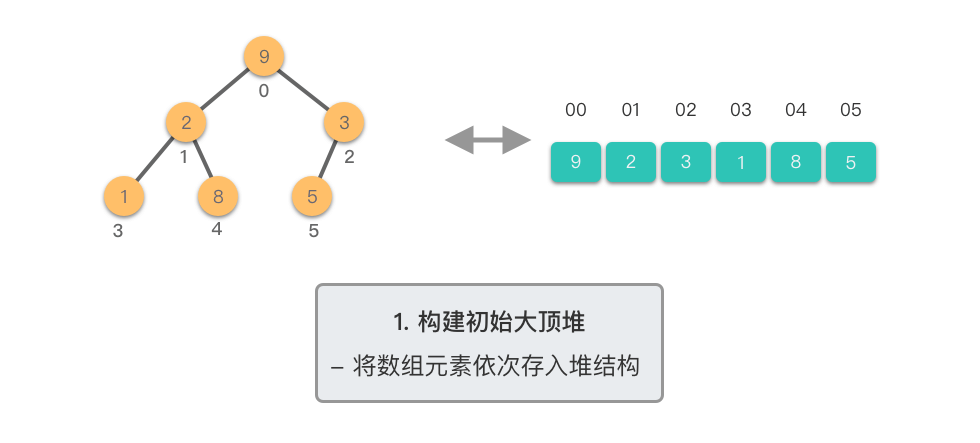
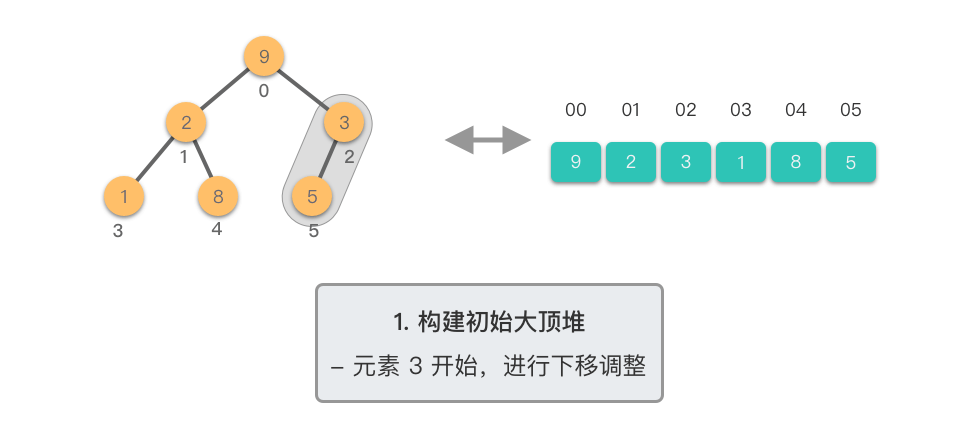
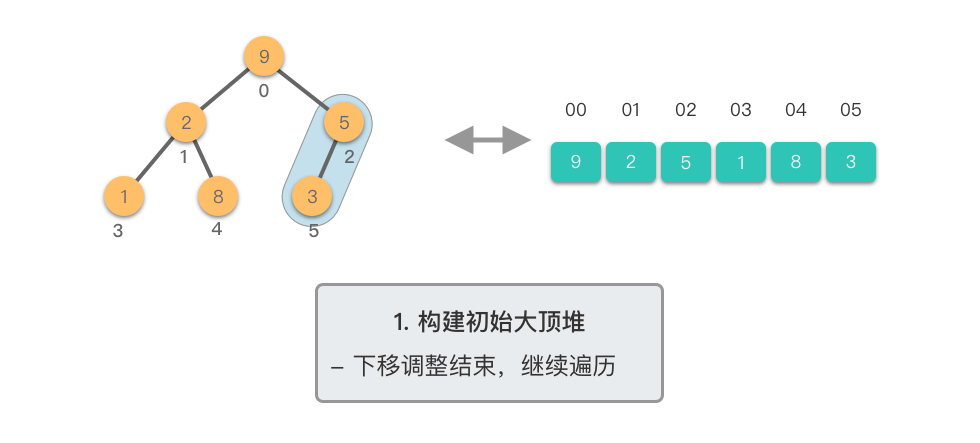
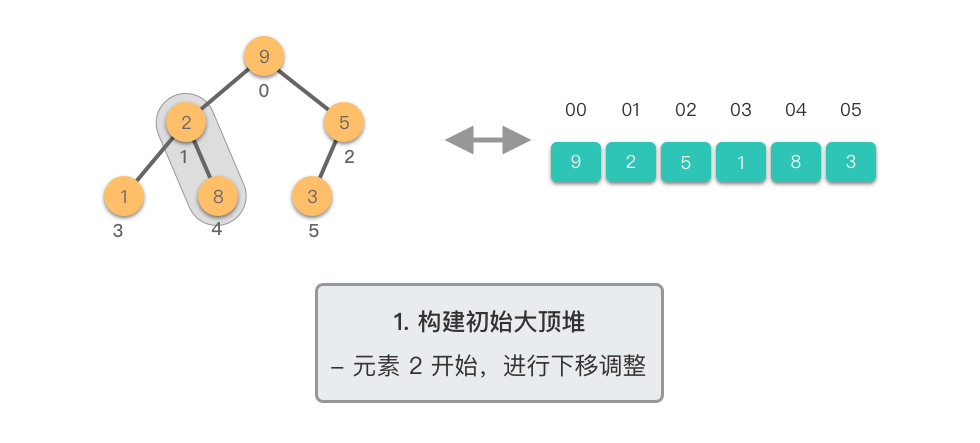
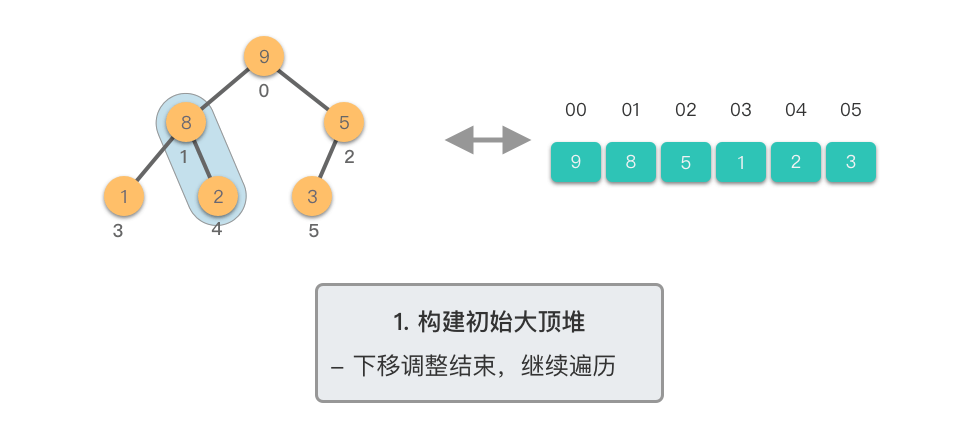
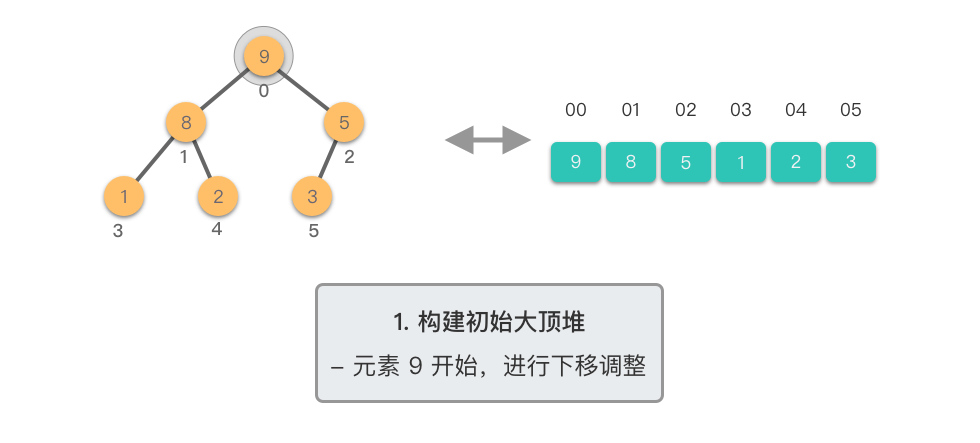
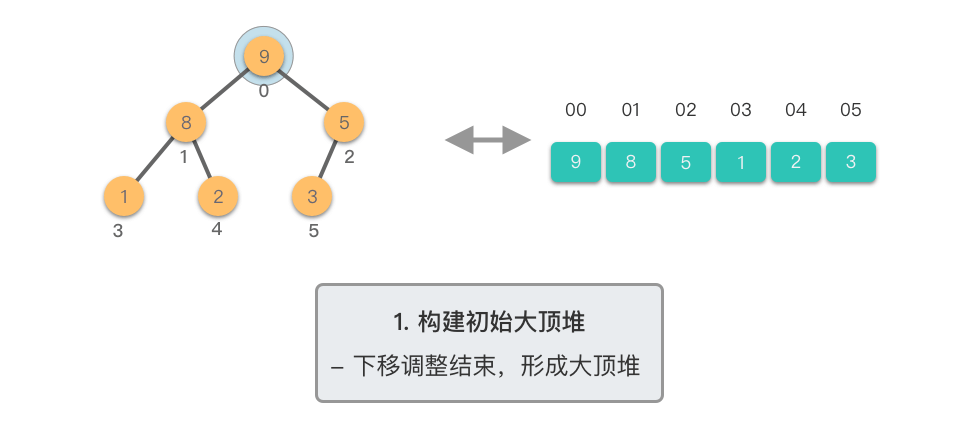
构建初始大顶堆:
- 定义一个数组实现的堆结构,将原始数组的元素依次存入堆结构的数组中(初始顺序不变)。
- 从数组的中间位置开始,从右至左,依次通过「下移调整」将数组转换为一个大顶堆。
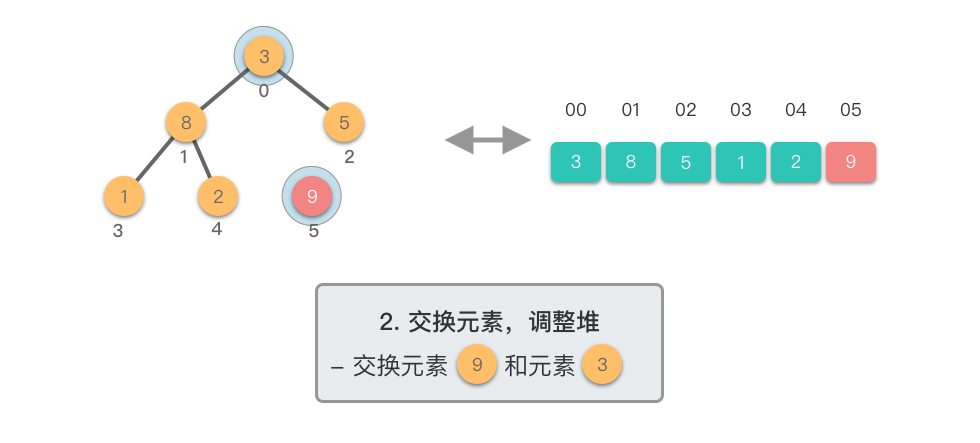
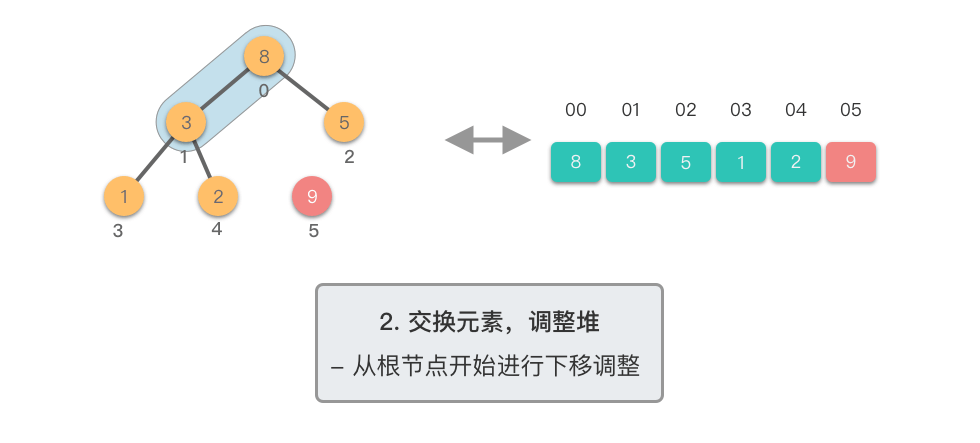
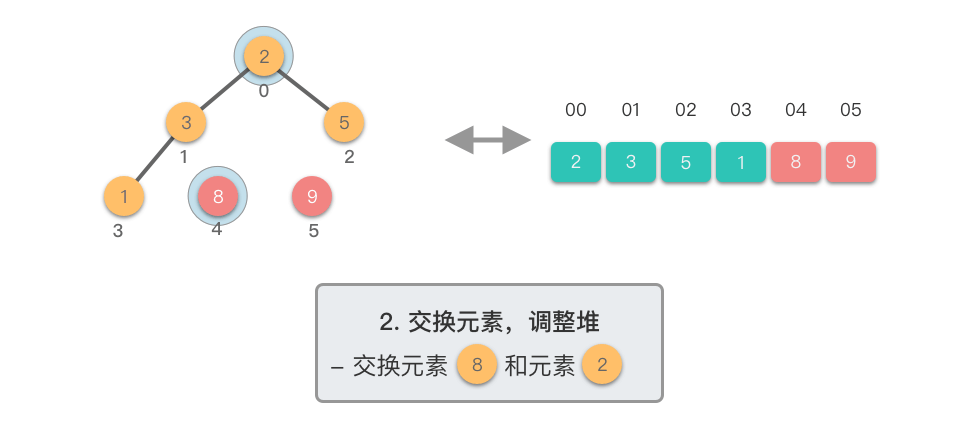
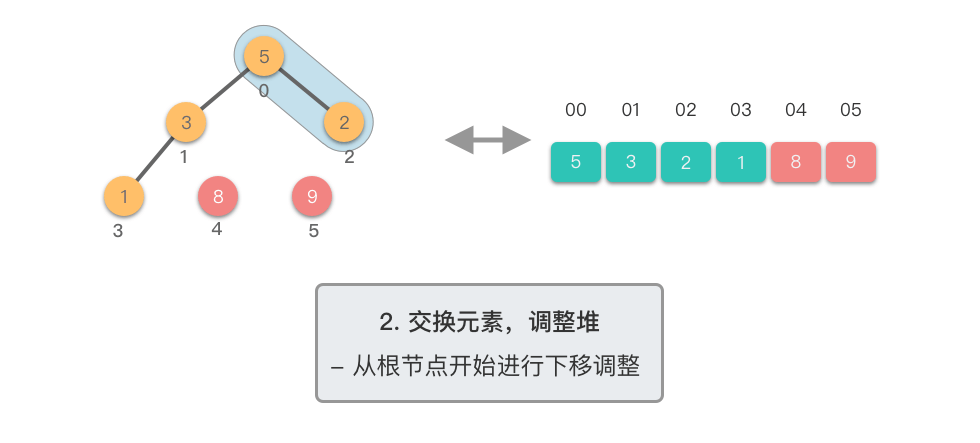
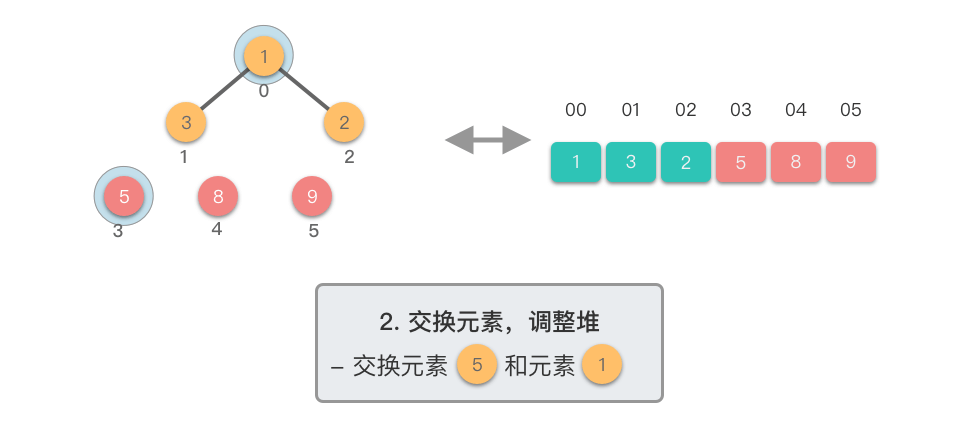
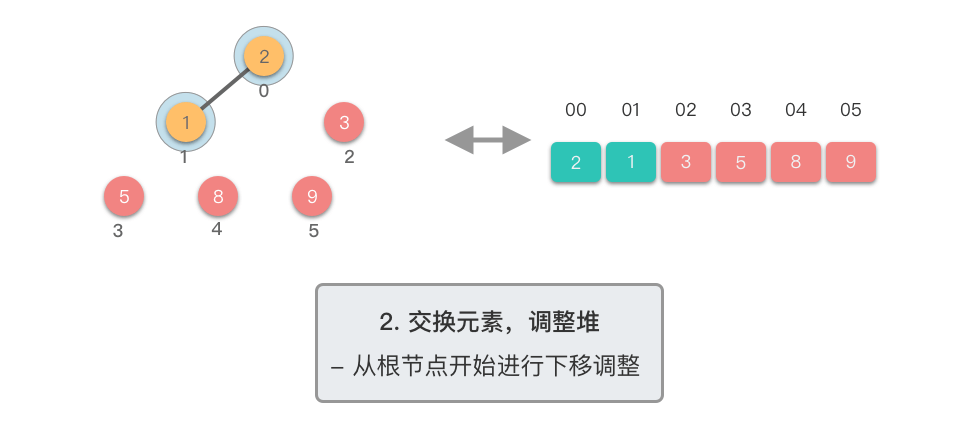
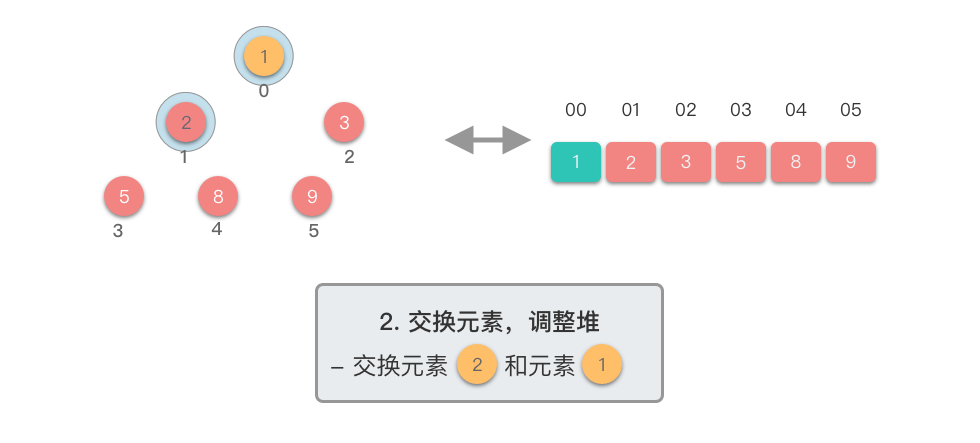
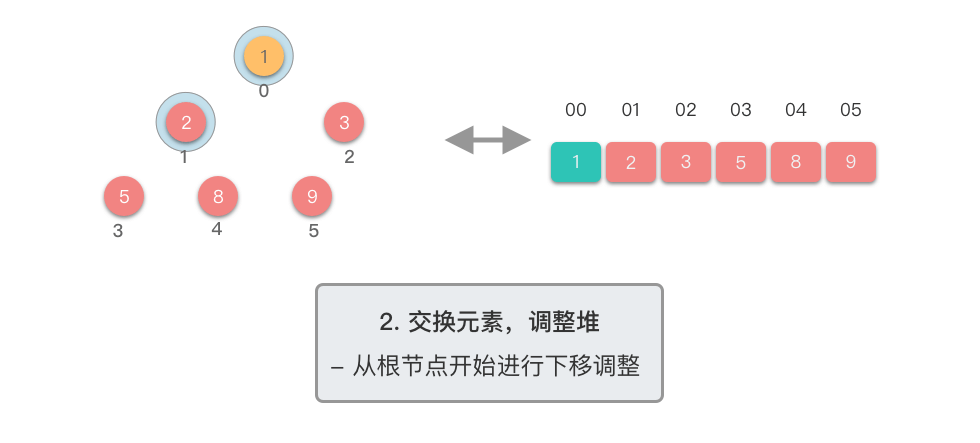
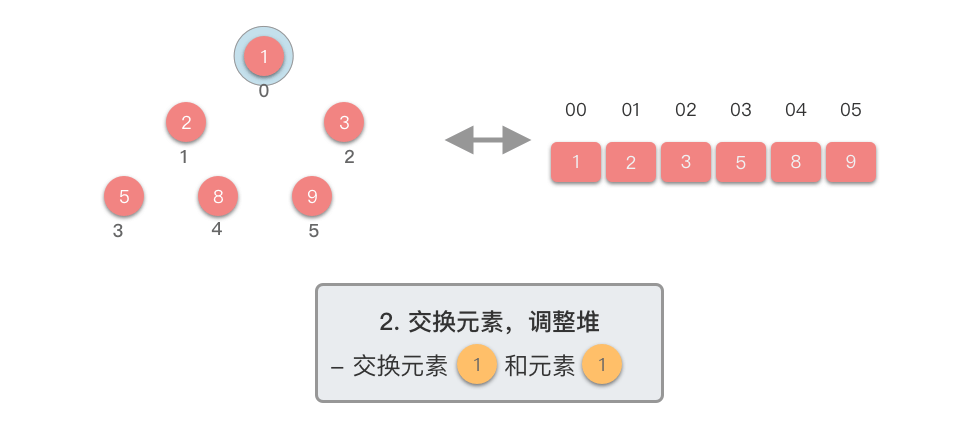
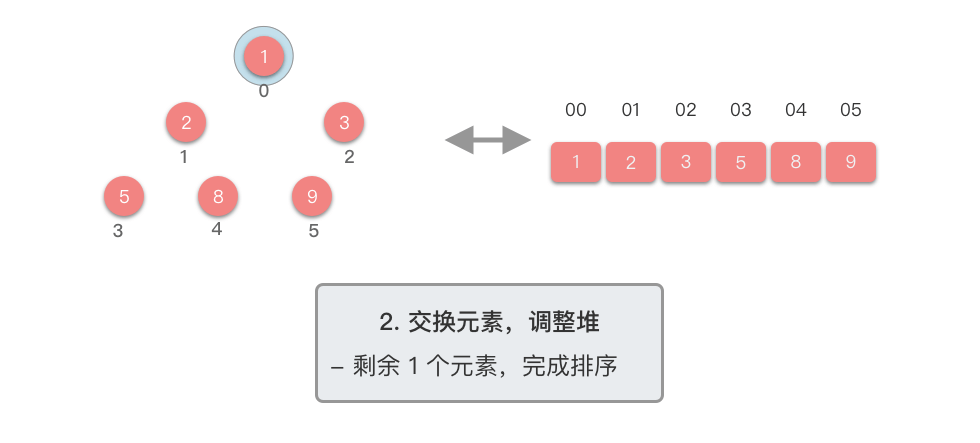
交换元素,调整堆:
- 交换堆顶元素(第
- 交换元素之后,由于堆顶元素发生了改变,需要从根节点开始,对当前堆进行「下移调整」,使其保持堆的特性。
- 交换堆顶元素(第
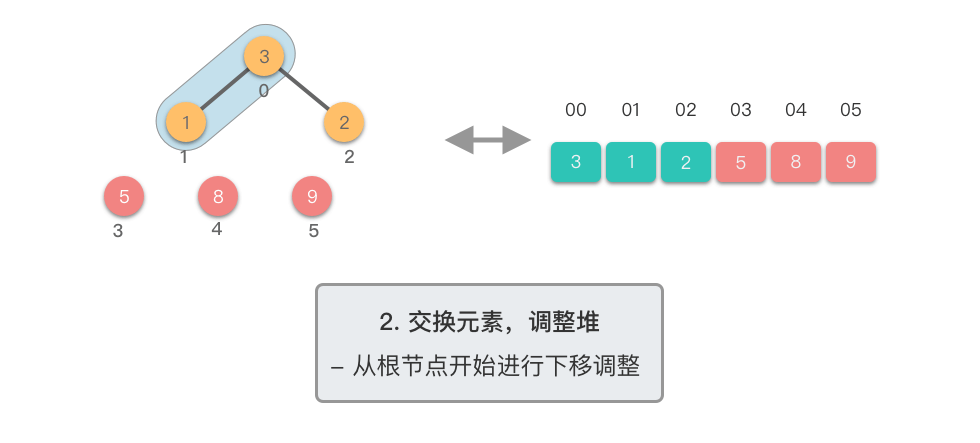
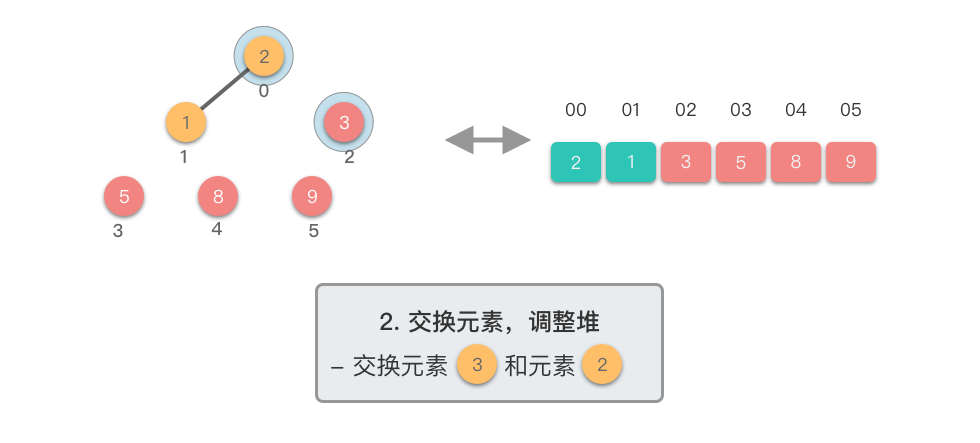
重复交换和调整堆:
- 重复第
- 重复第
::: tabs#heapSortBuildMaxHeap
@tab <1>
@tab <2>
@tab <3>
@tab <4>
@tab <5>
@tab <6>
@tab <7>
:::
::: tabs#heapSortExchangeVal
@tab <1>
@tab <2>
@tab <3>
@tab <4>
@tab <5>
@tab <6>
@tab <7>
@tab <8>
@tab <9>
@tab <10>
@tab <11>
@tab <12>
:::
2.3 堆排序代码实现
class MaxHeap:
......
def __buildMaxHeap(self, nums: [int]):
size = len(nums)
# 先将数组 nums 的元素按顺序添加到 max_heap 中
for i in range(size):
self.max_heap.append(nums[i])
# 从最后一个非叶子节点开始,进行下移调整
for i in range((size - 2) // 2, -1, -1):
self.__shift_down(i, size)
def maxHeapSort(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
# 根据数组 nums 建立初始堆
self.__buildMaxHeap(nums)
size = len(self.max_heap)
for i in range(size - 1, -1, -1):
# 交换根节点与当前堆的最后一个节点
self.max_heap[0], self.max_heap[i] = self.max_heap[i], self.max_heap[0]
# 从根节点开始,对当前堆进行下移调整
self.__shift_down(0, i)
# 返回排序后的数组
return self.max_heap
class Solution:
def maxHeapSort(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
return MaxHeap().maxHeapSort(nums)
def sortArray(self, nums: [int]) -> [int]:
return self.maxHeapSort(nums)
print(Solution().sortArray([10, 25, 6, 8, 7, 1, 20, 23, 16, 19, 17, 3, 18, 14]))2.4 堆排序算法分析
- 时间复杂度:
- 堆积排序的时间主要花费在两个方面:「建立初始堆」和「下移调整」。
- 设原始数组所对应的完全二叉树深度为
- 在第
- 在第
- 在第
- 因此,堆积排序的时间复杂度为
- 空间复杂度:
- 排序稳定性:在进行「下移调整」时,相等元素的相对位置可能会发生变化。因此,堆排序是一种 不稳定排序算法。
来源:https://github.com/itcharge/LeetCode-Py