15.MyBatis入门系列(15) -MyBatis运行原理之SQL查询源码分析
15.MyBatis入门系列(15) -MyBatis运行原理之SQL查询源码分析
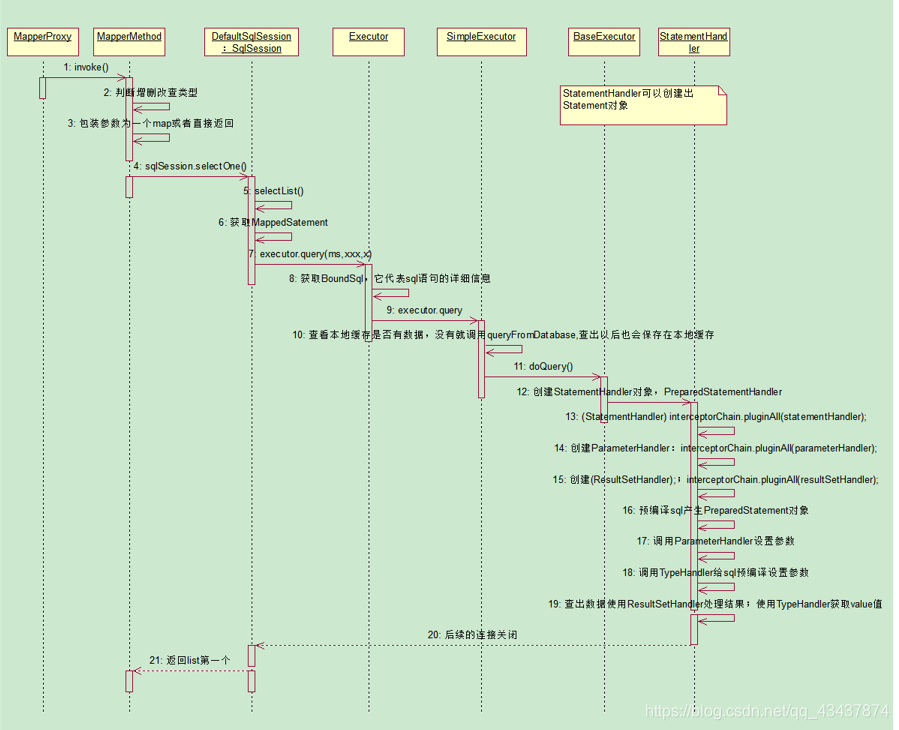
查询流程
在通过代理模式获取到mapper接口的代理对象后,就可以直接使用代理对象调用mappper方法进行增删改查操作了。
List<User> dynamicUserList = userMapper.selectDynamicUserList(userQuery);流程图
源码分析
1. 代理对象invoke
代理对象执行时,会进入MapperProxy类invoke方法。
/**
* 执行代理 代理以后,所有Mapper的方法调用时,都会调用这个invoke方法
*
* @param proxy 代理对象
* @param method 执行方法
* @param args 方法参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 并不是任何一个方法都需要执行调用代理对象进行执行,如果这个方法是Object中通用的方法(toString、hashCode等)无需执行
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 代理执行
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}2. 对Mapper方法进行处理
判断不是Object中的方法后,进入cachedInvoker(method)方法对method进行处理,返回一个MapperMethodInvoker对象。MapperMethodInvoker可以理解为真实的执行方法对象。
因为当前Method是JDK中的类,无法进行进行数据库复杂操作,需要进行进一步处理。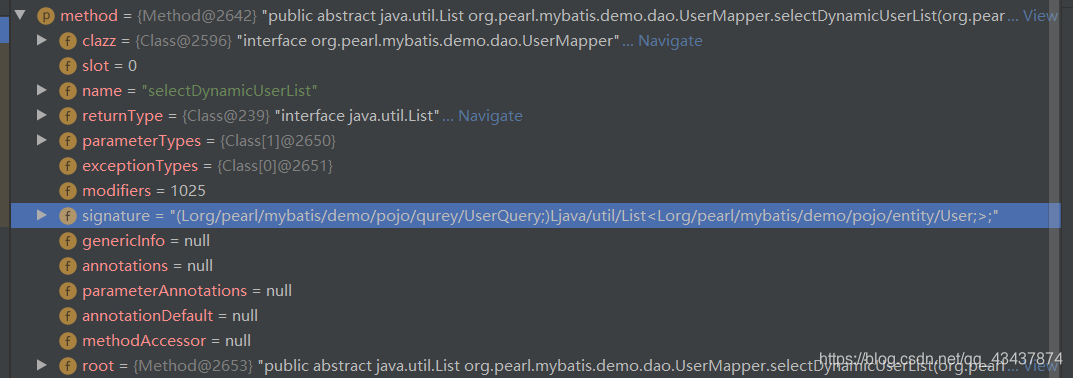
/**
* @param method 方法对象
* @return MapperMethodInvoker
* @throws Throwable
*/
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method,
// 处理方法
m -> {
// 如果是接口中的default修饰的方法
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// 非default方法返回一个PlainMethodInvoker
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}3. Method转为MapperMethod
在第二步cachedInvoker方法中返回MapperMethodInvoker 时,首先创建了一个MapperMethod对象。MapperMethod是对Mapper接口中的方法结合当前sqlSession中的Configuration对象,进一步处理为Mybatis中能执行操作的方法对象。
// 非default方法返回一个PlainMethodInvoker
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));MapperMethod的有参构造,创建了SqlCommand和MethodSignature两个对象并赋值给MapperMethod的成员变量。
/***
* 构造方法
* @param mapperInterface mapper接口
* @param method 执行方法对象
* @param config Configuration对象
*/
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}4. 创建SqlCommand对象
SqlCommand对象有两个重要的属性name和type,name存放MappedStatement的ID,type存放当前的增删改查类型。
public static class SqlCommand {
private final String name; // org.pearl.mybatis.demo.dao.UserMapper.selectDynamicUserList
private final SqlCommandType type; // UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH
/**
* SqlCommand 对象
*/
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// 方法名 selectDynamicUserList
final String methodName = method.getName();
// 接口 interface org.pearl.mybatis.demo.dao.UserMapper
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
// 获取MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
// MappedStatement为null
if (ms == null) {
// 判断方法上是否有Flush注解
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
// 设置当前SqlCommand 的name 和 type属性
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}5. 获取MappedStatement
通过之前构建SqlSessionFactory源码分析中,我们了解到每个方法对应的MappedStatement都存放到了Configuration对象中名为mappedStatements的Map中,每个键值对存放了当前方法的ID及方法其他属性。
SqlCommand对象中的name就对应MappedStatement的ID。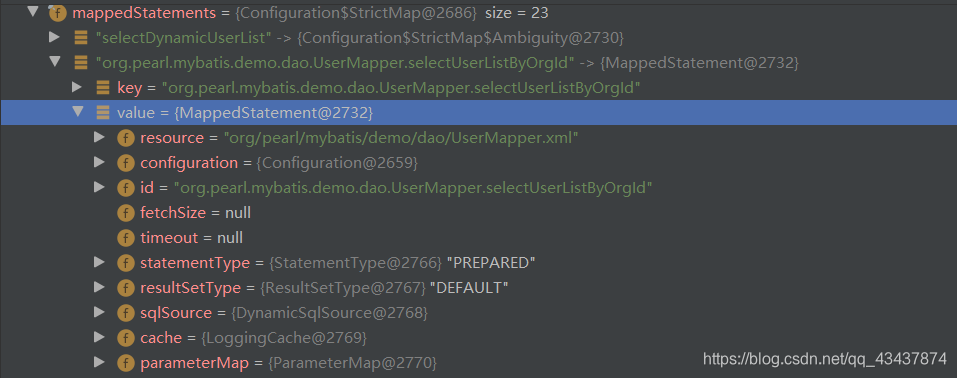
MapperMethod类中的resolveMappedStatement会从mappedStatements中获取改执行方法对应的MappedStatement。
/**
* 获取MappedStatement
*/
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,
Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
// ID org.pearl.mybatis.demo.dao.UserMapper.selectDynamicUserList
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
// 判断configuration 是否有该MappedStatement
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
// 有直接获取并返回
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
return null;
}
// 没有MappedStatement 递归创建
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}MapperMethod的构造方法中,通过4、5两个步骤,就创建了SqlCommand对象,此对象主要记录了执行方法的MappedStatement的ID及操作类型。
6. 创建MethodSignature对象
MapperMethod的构造方法,接下来会创建MethodSignature对象。
MethodSignature方法签名类,主要提供存放当前方法的返回值类型,处理参数等功能。
/**
* 方法签名,静态内部类
*/
public static class MethodSignature {
// 是否多值查询
private final boolean returnsMany;
// 是否map查询
private final boolean returnsMap;
// 是否void查询
private final boolean returnsVoid;
// 是否游标查询
private final boolean returnsCursor;
// 是否Optional
private final boolean returnsOptional;
// 返回类型
private final Class<?> returnType;
// 获取mapKey的值
private final String mapKey;
// ResultHandler类型在method参数的序号
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
// 分页参数在method参数的序号
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
// 参数名称解析器
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// 解析返回的类型 interface java.util.List
Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface);
// 设置返回类型到 方法签名中
if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType;
} else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType();
} else {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
}
// 设置方法签名相关属性
this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsMany = configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray();
this.returnsCursor = Cursor.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsOptional = Optional.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);
this.returnsMap = this.mapKey != null;
// Mybatis默认的分页是通过RowBounds参数来实现的,并且是在内存里面进行的
// 如果方法参数中包含RowBounds类型或其子类型的参数,找出这个参数在方法参数列表中的下标值
this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);
// 如果方法参数中包含ResultHandler类型或其子类型的参数,找出这个参数在方法参数列表中的下标值
this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);
// 参数名称解析器
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}7. MethodSignature参数名称解析器
在MethodSignature创建了一个ParamNameResolver参数名解析器。主要用来处理接口形式的参数,最后会把参数处放在一个map中。
在配置文件中有一个useActualParamName配置,参数名称解析器有用到,这个配置的意思是是否使用真实的参数名,比如(User user), 就会获取到user这个名称。但是javac编译后后,会优化,再通过反射获取,其名称就不是user了。
<setting name="useActualParamName" value="true" />可以看到实际运行时,获取到的参数名是arg0。
ParamNameResolver成员属性:
// Param 注解前缀
public static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
// 是否使用实际传入的参数名
private final boolean useActualParamName;
// 存放参数的位置和对应的参数名
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
// 是否使用@param注解
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;ParamNameResolver构造方法解析参数逻辑:
/**
* 参数名解析器
* 主要用来处理接口形式的参数,最后会把参数处放在一个map中
*
* @param config Configuration
* @param method Method
*/
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
// 获取Configuration中的useActualParamName属性 true
this.useActualParamName = config.isUseActualParamName();
// 参数的类型数组
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 方法注解的二维数组,每一个方法的参数包含一个注解数组。
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
// 创建一个有序的Map
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
// 方法注解的集合的长度
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
// 循环注解,没有注解时,paramCount为1
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
// 如果为特殊参数(RowBounds(分页对象) 和 ResultHandler(结果处理)),则不会记入mapper的实际参数
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
//判断参数是否由@Param注解修饰,如果有Param注解 hasParamAnnotation = true,参数的名称为Param定义的值
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
// 没有Param注解
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
//如果配置了useActualParamName=true的话,则取实际参数的名称 arg0
if (useActualParamName) {
//
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
//否则,该参数的名称为0,1....n
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
// 将参数序列号 参数名放入有序Map中 { 0 ,arg0}
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
// 将Map 赋值给names
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}构建完参数解析器后,MethodSignature方法签名对象就构建完成了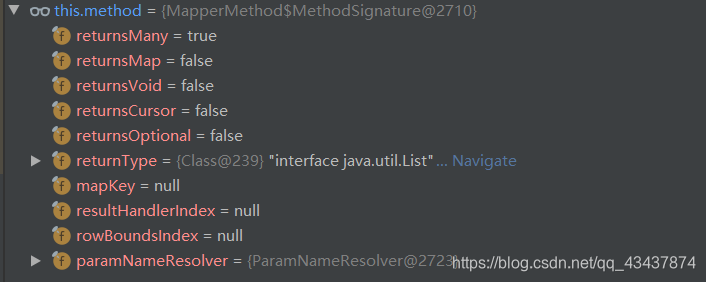
8. 构建PlainMethodInvoker对象
SqlCommand及MethodSignature对象构建完成后,MapperMethod对象也就完成了初始化,第2步中的cachedInvoker(method),就只有就有一步了,构建PlainMethodInvoker对象。
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));通过对mapper方法的重重处理,最后获取PlainMethodInvoker对象。
构造方法很简单,就是把处理后的MapperMethod方赋值给成员属性。
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}9. 第二个invoke
PlainMethodInvoker创建成功后,拥有了MapperMethod对象,最终回到第1步代码中,调用PlainMethodInvoker的 invoke方法,开始执行正删改查。
// 代理执行
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);而PlainMethodInvoker.invoke,实际调用的是内部成员mapperMethod的execute(sqlSession, args)方法。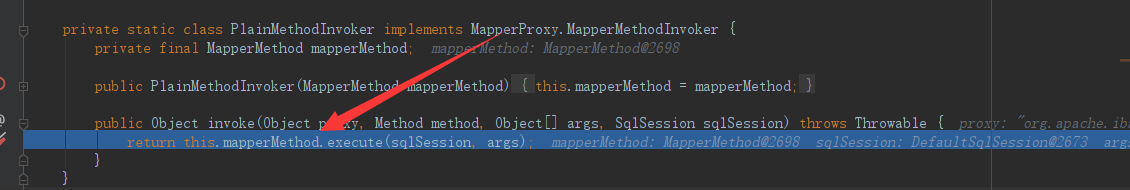
10. 判断操作类型
MapperMethod中的execute方法执行操作,会根据不同的操作类型执行不同的方法。
/**
* 执行增删改查
*
* @param sqlSession SqlSession
* @param args 实际参数 UserQuery(userId=null, userName=null, userName_like=null, loginName=zhangwei, phone=null, email=null)
* @return
*/
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
// 获取操作类型
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
// 查询操作
case SELECT:
// 根据不同的返回类型 ,执行不同方法
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
// 返回多个对象
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
// 执行查询
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
// 返回的结果集
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}11. executeForMany查询多个结果集
因为我们查询的是list,所有会进入executeForMany方法进行查询操作。
/**
* 查询多个结果集
*
* @param sqlSession SqlSession
* @param args args 参数集合
*/
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
// 将args转为SqlCommandParam
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// RowBounds 分页查询
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
// 调用sqlSession查询方法
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
// 处理返回数组 当返回的List 和方法返回类型不太匹配时
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}11. 调用sqlSession查询方法
第10步中,最后调用了 sqlSession.selectList方法,进行最终的操作。
/**
* 查询列表
*
* @param statement MappedStatement
* @param parameter 参数
* @param rowBounds 分页
* @param handler 结果处理器
* @return List
*/
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
// 获取MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 执行器查询
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}12. 执行器执行查询
之前说过,最终的查询是由执行器去进行操作了的,selectList方法实际调用的是执行器的query方法。因为我们开启了缓存,所以执行器是CachingExecutor。
/**
* 缓存执行器查询
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 获取缓存的Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}13. 获取BoundSql 对象
执行器进行query查询时,第一步是通过MappedStatement获取了BoundSql 对象。
/**
* 获取 BoundSql
*/
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 通过SqlSource获取BoundSql对象
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 参数映射
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// 检查参数映射中的嵌套结果映射
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}BoundSql 对象是通过MappedStatement中的sqlSource对象去获取的。SqlSource是一个接口,我们这里是动态查询,所以会调用DynamicSqlSource。
// 通过SqlSource获取BoundSql对象
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject); //得到绑定的SQL
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
//生成一个动态上下文
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
//这里SqlNode.apply只是将${}这种参数替换掉,并没有替换#{}这种参数
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
//调用SqlSourceBuilder
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
//SqlSourceBuilder.parse,注意这里返回的是StaticSqlSource,解析完了就把那些参数都替换成?了,也就是最基本的JDBC的SQL写法
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
//看似是又去递归调用SqlSource.getBoundSql,其实因为是StaticSqlSource,所以没问题,不是递归调用
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {
boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return boundSql;
}最后返回BoundSql对象。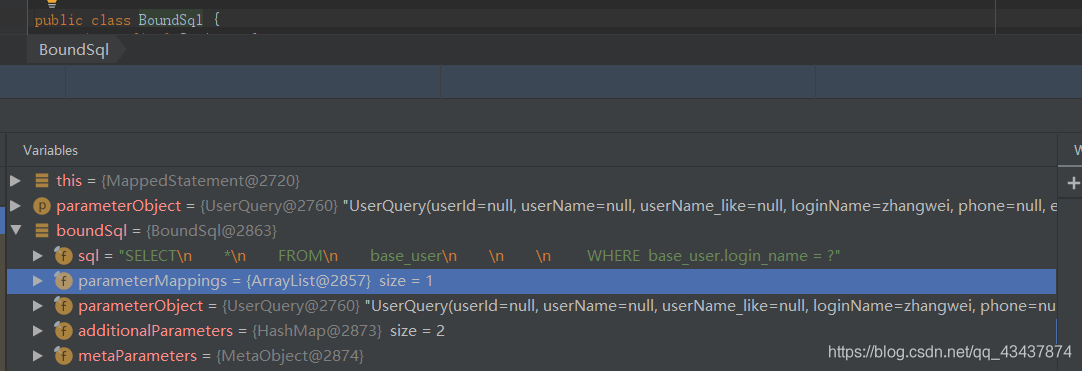
BoundSql 中就是对解析后的sql描述,包括对动态标签的解析,并且将 #{} 解析为占位符 ? ,还包含参数的描述信息。这个类没有什么复杂操作,可以看作是解析后的sql描述对象。
/**
* An actual SQL String got from an {@link SqlSource} after having processed any dynamic content.
* The SQL may have SQL placeholders "?" and an list (ordered) of an parameter mappings
* with the additional information for each parameter (at least the property name of the input object to read
* the value from).
* <p>
* Can also have additional parameters that are created by the dynamic language (for loops, bind...).
*
* 经过处理一些动态sql的部分获取到的真实sql,这个sql可能还有占位符?和一个参数映射的有序集合,并且还有每个参数的额外信息
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class BoundSql {
// 最终解析的sql,Mybatis将#{}和${}解析后的sql,其中#{}会被解析为?
private final String sql;
// 参数映射
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
// 参数对象
private final Object parameterObject;
// 额外的参数
private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters;
// 元数据参数
private final MetaObject metaParameters;
public BoundSql(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings, Object parameterObject) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.parameterObject = parameterObject;
this.additionalParameters = new HashMap<>();
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
public List<ParameterMapping> getParameterMappings() {
return parameterMappings;
}
public Object getParameterObject() {
return parameterObject;
}
public boolean hasAdditionalParameter(String name) {
String paramName = new PropertyTokenizer(name).getName();
return additionalParameters.containsKey(paramName);
}
public void setAdditionalParameter(String name, Object value) {
metaParameters.setValue(name, value);
}
public Object getAdditionalParameter(String name) {
return metaParameters.getValue(name);
}
}14. 获取缓存的Key
获取BoundSql 对象后,下一步就是获取缓存的Key,在cache中唯一确定一个缓存项需要使用缓存项的key,Mybatis中因为涉及到动态SQL等多方面因素,其缓存项的key不等仅仅通过一个String表示,所以MyBatis 提供了CacheKey类来表示缓存项的key,在一个CacheKey对象中可以封装多个影响缓存项的因素。
CacheKey key = this.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);Key:
87892607:-776139895:org.pearl.mybatis.demo.dao.UserMapper.selectDynamicUserList:0:2147483647:SELECT
*
FROM
base_user
WHERE base_user.login_name = ?:zhangwei:development15. 执行器进行查询
获取了key后,最终执行器进行query查询。
/**
* 查询
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 获取缓存对象
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// /查CacheKey,查不到再委托给实际的执行器去查
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
// 查询
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}继续调用BaseExecutor的query
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
//如果已经关闭,报错
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//先清局部缓存,再查询.但仅查询堆栈为0,才清。为了处理递归调用
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
//加一,这样递归调用到上面的时候就不会再清局部缓存了
queryStack++;
//先根据cachekey从localCache去查
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
//若查到localCache缓存,处理localOutputParameterCache
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//从数据库查
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
//清空堆栈
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
//延迟加载队列中所有元素
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
//清空延迟加载队列
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
//如果是STATEMENT,清本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}16. 数据库查询
先去查询二级缓存,二级没有,查询本地缓存,本地缓存中还没有,才 会从数据库进行查询。
//从数据库查
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//先向缓存中放入占位符???
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//最后删除占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//加入缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
//如果是存储过程,OUT参数也加入缓存
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}继续调用SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法。Statement 是java.sql中的接口,所以底层还是用的原生的JDBC,newStatementHandler会创建StatementHandler,是四大组件之一。StatementHandler创建时也会使用拦截器进行包装。
//select
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//新建一个StatementHandler
//这里看到ResultHandler传入了
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//准备语句
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//StatementHandler.query
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}之后通过PreparedStatement的execute查询,
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement)statement;
ps.execute();
return this.resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}17. 结果处理器
Statement 进行操作后,结果处理器会对Statement 进行处理,封装结果集,然后返回,整个流程就走的差不多了,这里面的细节后续介绍。。。因为实在太多了。。。有参数处理器,结果处理器,类型处理器等...
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(this.mappedStatement.getId());
List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = this.getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = this.mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
this.validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while(rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = (ResultMap)resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, (ResultMapping)null);
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
String[] resultSets = this.mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while(rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = (ResultMapping)this.nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = this.configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, (List)null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
}
return this.collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}总结
一次简单的查询,竟然走了这么远。。。而且以上只是还不够深入,其他细节以后慢慢在介绍。。。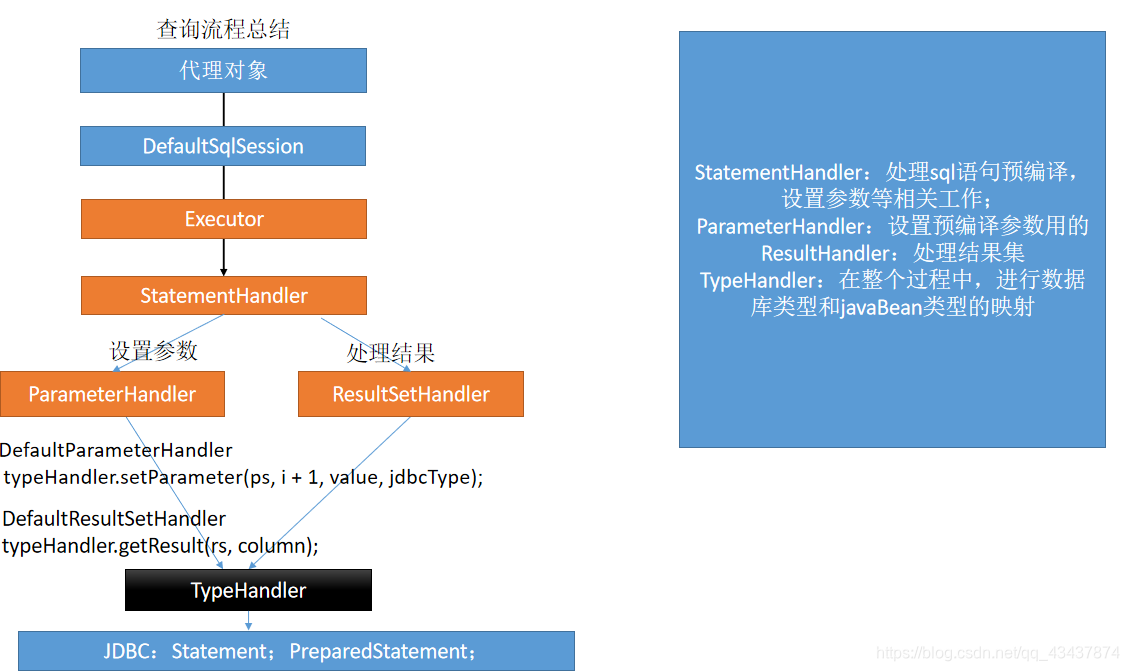
来源:https://yunyanchengyu.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118160518