04.netty入门(四) Channel介绍及应用
04.netty入门(四) Channel介绍及应用
Channel(通道)介绍
- NIO的通道类似于流,但有些区别如下:
- 通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写;
- 通道可以实现异步读写数据;
- 通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲;

- BIO中的stream是单向的,例如FileInputStream对象只能进行读取数据的操作,而NIO中的通道(Channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作。
- Channel在NIO中是一个接口 public interface Channel extends Closeable{}
- 常用的Channel类有:FileChannel、DatagramChannel、ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel。
- FileChannel用于文件的数据读写,DatagramChannel用于UDP的数据读写,ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel用于TCP的数据读写。
FileChannel类
FileChannel主要用来对本地文件进行IO操作,常见的方法有
- public int read(ByteBuffer dst)// 从通道读取数据并放到缓冲区中
- public int write(ByteBuffer src)// 把缓冲区的数据写到通道中
- public long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel var1, long var2, long var4)// 从目标通道中复制数据到当前通道
- public long transferTo(long var1, long var3, WritableByteChannel var5)// 把数据从当前通道复制给目标通道
通道(Channel)案例1
需求:
(1)使用前面学习的ByteBuffer(缓冲)和FileChannel(通道),将"hello,everybody"写入到text01.txt文件中。
(2)文件不存在就创建。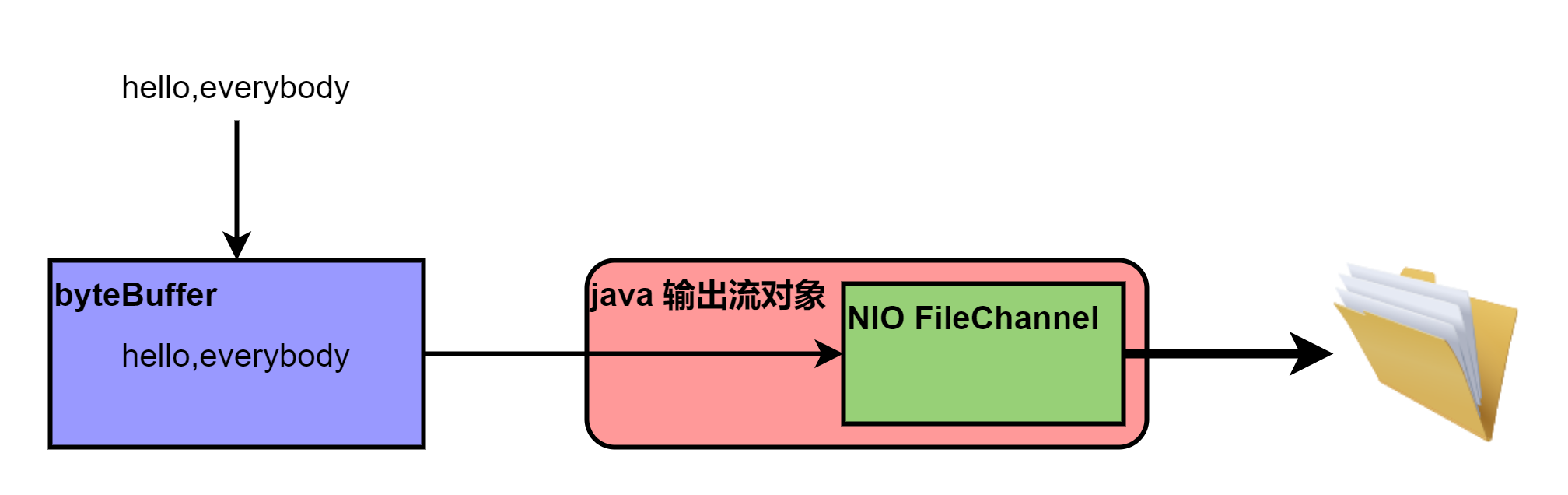
public class NIOFileChannel01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str = "hello, everybody";
// 创建一个输出流 -> channel
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\text01.txt");
// 通过输出流fileOutputStream获取对应的文件channel
FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
// 创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将str放入byteBuffer
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
// 对byteBuffer进行flip
byteBuffer.flip();
// 将byteBuffer 数据写入到channel中
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
// 关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}通道(Channel)案例2
需求:
(1)使用前面学习的ByteBuffer(缓冲)和FileChannel(通道),将text01.txt文件中的数据读入到程序中,并显示在控制台屏幕。
(2)假定文件已经存在。
public class NIOFileChannel02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建文件的输入流
File file = new File("d:\\text01.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// 通过fileInputStream 获取对应的FileChannel -> 实际类型 FileChannelImpl
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
// 创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
// 将通道的数据读入到buffer中
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
// 将 byteBuffer的字节数据转成String
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
//关闭流
fileInputStream.close();
}
}通道(Channel)案例3-使用一个Buffer完成文件读取
需求:
(1)使用FileChannel(通道)和方法read、write,完成文件的拷贝。
(2)拷贝一个文本文件1.txt,放在项目下即可。
public class NIOFileChannel03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel01 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("2.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel02 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
// 循环读取
while (true) {
// 重要操作, byteBuffer重置
byteBuffer.clear();
int read = fileChannel01.read(byteBuffer);
if (read == -1) {// 读取结束
break;
}
// 将buffer中的数据写入到fileChannel02 --> 2.txt
byteBuffer.flip();
fileChannel02.write(byteBuffer);
}
// 关闭通道和流
fileChannel01.close();
fileChannel02.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}通道(Channel)案例4-拷贝文件tranferFrom方法
需求:
(1)使用FileCHannel(通道)和方法transferFrom,完成文件的拷贝。
(2)拷贝一张图片。
public class NIOFileChannel04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建相关流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\a.png");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\a2.png");
// 获取各个流对应的fileChannel
FileChannel sourceChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
// 使用trandferFrom完成拷贝
destChannel.transferFrom(sourceChannel, 0, sourceChannel.size());
// 关闭相关通道和流
sourceChannel.close();
destChannel.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}关于Buffer和Channel的注意事项和细节
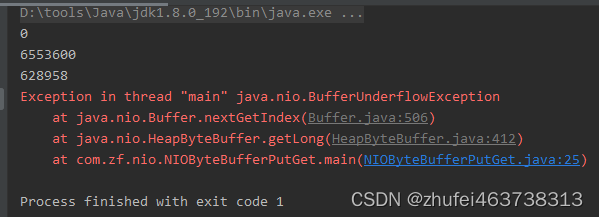
- ByteBuffer支持类型化的put和get,put放入的是什么数据类型,get就应该使用相应的数据类型来取出,否则可能有BufferUnderflowException异常。
public class NIOByteBufferPutGet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
// 类型化方式放入数据
byteBuffer.putInt(100);
byteBuffer.putLong(9);
byteBuffer.putChar('飞');
byteBuffer.putShort((short) 4);
// 取出
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getShort());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getInt());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getLong());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getLong());
}
}
- 可以将一个普通Buffer转成只读Buffer。
public class ReadOnlyBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
byteBuffer.put((byte) i);
}
// 读取
byteBuffer.flip();
// 得到一个只读的Buffer
ByteBuffer readOnlyBuffer = byteBuffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.getClass());
while (readOnlyBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.get());
}
// 此处报ReadOnlyBufferException异常
readOnlyBuffer.put((byte) 500);
}
}- NIO还提供了MappedByteBuffer,可以让文件直接在内存(堆外的内存)中进行修改,而如何同步到文件由NIO来完成。
/**
* 说明:
* 1.MappedByteBuffer可以让文件直接在内存(堆外内存)中修改,操作系统不需要拷贝一次
*/
public class MappedByteBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw");
// 获取对应的通道
FileChannel channel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
/**
* 参数1:FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE,使用的是读写模式
* 参数2: 0,代表可以修改的起始位置
* 参数3: 5,是映射到内存的大小,即将文件1.txt的多少个字节映射到内存
* 可以直接修改的范围就是 0-5
* 实际类型 DirectByteBuffer
*/
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
mappedByteBuffer.put(0, (byte) 'H');
mappedByteBuffer.put(3, (byte) '9');
// 关闭
randomAccessFile.close();
System.out.println("修改成功");
}
}- NIO还支持通过多个Buffer(即Buffer数组)完成读写操作,即Scattering和Gatering。
/**
* Scattering:将数据写入到buffer时,可以采用buffer数组,依次写入
* Gathering:从buffer读取数据时,可以采用buffer数组,依次读
*/
public class ScatteringAndGatheringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel网络
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);
// 绑定端口到Socket,并启动
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
// 创建Buffer数组
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
// 等待客户端连接(telnet)
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
// 假定接收从客户端接收8个字节
int messageLength = 8;
// 循环的读取
while (true) {
int byteRead = 0;
while (byteRead < messageLength) {
long readCount = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
// 累计读取的字节数
byteRead += readCount;
System.out.println("byteRead=" + byteRead);
// 使用流打印, 看看当前的这个buffer的position和limit
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).stream()
.map(buffer -> "position=" + buffer.position() + " ,limit=" + buffer.limit())
.forEach(System.out::println);
// 将所有的buffer进行反转
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(buffer -> buffer.flip());
// 将数据读出,显示到客户端
long byteWrite = 0;
while (byteWrite < messageLength) {
long writeCount = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite += writeCount;
}
// 将所有的buffer进行clear操作
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(buffer -> buffer.clear());
System.out.println("byteRead=" + byteRead + " ,byteWrite=" + byteWrite + ", messageLength=" + messageLength);
}
}
}
}使用telnet进行测试,打开cmd命令行窗口,连接命令:telnet 127.0.0.1 7000
发送消息快捷键 ctrl+]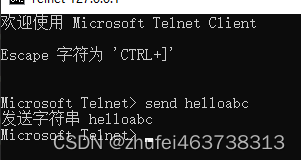

来源:https://blog.csdn.net/zhufei463738313/article/details/129054723