54.Spring Boot 监控工具 Admin 入门
54.Spring Boot 监控工具 Admin 入门
1. 概述
在《Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》中,我们学习了通过 Actuator 端点,通过 HTTP 请求,获得应用的审计(auditing)、健康状况(health)和指标(metrics)等数据。
不过正如我们在文末所说,直接请求 Actuator 端口,查看监控数据,是非常低效且使用体验较差的。所以我们的一个解决方案是 Spring Boot Admin 监控工具,也是本文我们要学习的。其官方文档介绍如下:
FROM 《Spring Boot Admin Reference Guide》
codecentric's Spring Boot Admin is a community project to manage and monitor your Spring Boot ® applications.
Spring Boot Admin 是由 https://github.com/codecentric 开源的一个社区项目,用于管理和监控 Spring Boot 应用。The applications register with our Spring Boot Admin Client (via HTTP) or are discovered using Spring Cloud ® (e.g. Eureka, Consul).
被监控和管理的应用程序,有两种方式注册到 Spring Boot Admin Server 上。
- 方式一,被监控和管理的应用程序,使用 Spring Boot Admin Client 库,通过 HTTP 调用注册到 Spring Boot Admin Server 上。
- 方式二,首先,被监控和管理的应用程序,注册到 Spring Cloud 集成的注册中心;然后 Spring Boot Admin Server 通过注册中心获取到被监控和管理的应用程序。
The UI is just a Vue.js application on top of the Spring Boot Actuator endpoints.
Spring Boot Admin Server UI 部分,采用 Vue 前端框架实现。
同时,Spring Boot Admin 是基于调用 Spring Boot Actuator 端点,进行实现的。
- 胖友认真看看艿艿上面的翻译噢,非直译。
2. 快速入门
本小节,我们来快速入门下 Spring Boot Admin 。一种会有两个项目:
- lab-35-admin-01-adminserver 项目,作为 Spring Boot Admin Server + UI ,在「2.1 Spring Boot Admin Server」中详细解析。
- lab-35-admin-01-demo-application 项目,示例项目,被监控和管理的应用程序,在「2.2 Spring Boot Admin Client」
其中,被监控和管理的应用程序,通过方式一 ,使用 Spring Boot Admin Client 库,通过 HTTP 调用注册到 Spring Boot Admin Server 上。
2.1 Spring Boot Admin Server
对应 lab-35-admin-01-adminserver 项目。
2.1.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-35-admin-01-adminserver</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 Spring Boot Admin Server 的自动化配置 -->
<!--
包含 1. spring-boot-admin-server :Server 端
2. spring-boot-admin-server-ui :UI 界面
3. spring-boot-admin-server-cloud :对 Spring Cloud 的接入
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>2.1.2 AdminServerApplication
创建 AdminServerApplication 类,用于启动 Spring Boot Admin Server。代码如下:
// AdminServerApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAdminServer
public class AdminServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AdminServerApplication.class, args);
}
}- 在类上,添加了
@EnableAdminServer注解,表示开启 Spring Boot Admin Server 功能。
2.1.3 简单测试
运行 #main(String[] args) 方法,启动 Spring Boot Admin Server。控制台输出日志如下:
2019-12-23 22:28:40.078 INFO 28796 --- [ main] o.s.b.web.embedded.netty.NettyWebServer : Netty started on port(s): 8080
2019-12-23 22:28:40.082 INFO 28796 --- [ main] c.i.s.l.a.AdminServerApplication : Started AdminServerApplication in 1.937 seconds (JVM running for 2.393)- 有没惊奇的发现,启动的 Server 是 Netty 。😈 Spring Boot Admin Server 采用 WebFlux 实现噢。
使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:8080/ 地址,访问 Spring Boot Admin Server UI 。界面如下:
- 比较友好的是,UI 界面目前支持中文,美滋滋。不过考虑到和 Spring Boot Actuator 更好的对应,所以我们还是切换到英文。
2.2 Spring Boot Admin Client
对应 lab-35-admin-01-demo-application 项目。
2.2.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-35-admin-01-demo-application</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 Spring MVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Actuator 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Spring Boot Admin Client 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>- 具体每个依赖的作用,胖友自己认真看下艿艿添加的所有注释噢。
2.2.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Spring Boot Admin Client 配置,如下:
management:
endpoints:
# Actuator HTTP 配置项,对应 WebEndpointProperties 配置类
web:
exposure:
include: '*' # 需要开放的端点。默认值只打开 health 和 info 两个端点。通过设置 * ,可以开放所有端点。
spring:
application:
name: demo-application # 应用名
boot:
admin:
client:
url: http://127.0.0.1:8080 # Spring Boot Admin Server 地址
server:
port: 18080 # 设置自定义 Server 端口,避免和 Spring Boot Admin Server 端口冲突。- 配置
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include = *,设置 Spring Boot Actuator 所有端点都开放。 - 配置
spring.application.name = demo-application,设置应用名。 - 【重点 】配置
spring.boot.admin.client.url = http://127.0.0.1:8080,设置 Spring Boot Admin Server 地址。 - 配置
server.port = 18080,设置自定义 Server 端口,避免和 Spring Boot Admin Server 端口冲突。
😈 友情提示,如果使用方式一来注册,可以使用 Nginx 做多个 Spring Boot Admin 节点的负载均衡,而项目中配置该负载均衡的地址,从而实现 Spring Boot Admin 的高可用。
2.2.3 DemoApplication
创建 DemoApplication 类,用于启动示例项目。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}2.2.4 简单测试
运行 #main(String[] args) 方法,启动示例项目。控制台输出日志如下:
2019-12-23 2318:22.958 INFO 30802 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 18080 (http) with context path ''
2019-12-23 2318:22.961 INFO 30802 --- [ main] c.i.s.l.actuatordemo.DemoApplication : Started DemoApplication in 1.915 seconds (JVM running for 2.518)
2019-12-23 2318:23.308 INFO 30802 --- [2)-192.168.3.44] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2019-12-23 2318:23.308 INFO 30802 --- [2)-192.168.3.44] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2019-12-23 2318:23.314 INFO 30802 --- [2)-192.168.3.44] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 6 ms
2019-12-23 2318:24.119 INFO 30802 --- [gistrationTask1] d.c.b.a.c.r.ApplicationRegistrator : Application registered itself as 278170067ddd- 重点看到最后一行日志,示例项目成功注册到 Spring Boot Admin Server 上。
此时,使用浏览器,再次打开 http://127.0.0.1:8080/ 地址,会发现该应用注册上。界面如下:
然后,使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:8080/journal 地址,可以看到日志报表。界面如下:
- 可以看到实例「278170067ddd」的 3 个事件日志,分别是 REGISTERED = 应用注册, STATUS_CHANGED (UP) = 应用状态变化成 UP , ENDPOINTS_DETECTED = 应用的 Actuator 端点被获取到。
3. 功能介绍
Spring Boot Admin 提供的功能挺强大的,基本所有 Actuator 端点提供的功能,都开发了相应的 UI 界面。其仓库介绍功能列表如下:
FROM https://github.com/codecentric/spring-boot-admin
It provides the following features for registered applications.
- Show health status
- Show details, like
- JVM & memory metrics
- micrometer.io metrics
- Datasource metrics
- Cache metrics
- Show build-info number
- Follow and download logfile
- View jvm system- & environment-properties
- View Spring Boot Configuration Properties
- Support for Spring Cloud's postable /env- &/refresh-endpoint
- Easy loglevel management
- Interact with JMX-beans
- View thread dump
- View http-traces
- View auditevents
- View http-endpoints
- View scheduled tasks
- View and delete active sessions (using spring-session)
- View Flyway / Liquibase database migrations
- Download heapdump
- Notification on status change (via e-mail, Slack, Hipchat, ...)
状态变更通知(通过电子邮件,Slack,Hipchat,......)- Event journal of status changes (non persistent)
状态更改的事件日志(非持久性)
- 英文比较简单,基本和 Actuator 端点能够一一对应上。😈 暂时就不翻译了,翻译了反倒增加理解的障碍。
继续「2. 快速入门」的示例,点击具体某个应用,进入该应用的监控与管理。如下图:
功能还是蛮丰富的,我们逐个菜单来看看。
3.1 Insights
3.1.1 Details
翻译为细节 。如下图:
对应多个 Actuator 端点,拼凑而成的界面。涉及元数据、健康状态、进程、线程、JVM GC、JVM 内存。
3.1.2 Metrics
翻译为性能 。如下图:
对应 metrics 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「6. metrics 端点」小节。
通过该界面,我们可以选择要查询的 Metrics ,点击「Add Metrics」按钮,确认添加。
3.1.3 Environment
翻译为环境 。如下图:
对应 env 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「11. env 端点」小节。
3.1.4 Beans
翻译为类 。如下图: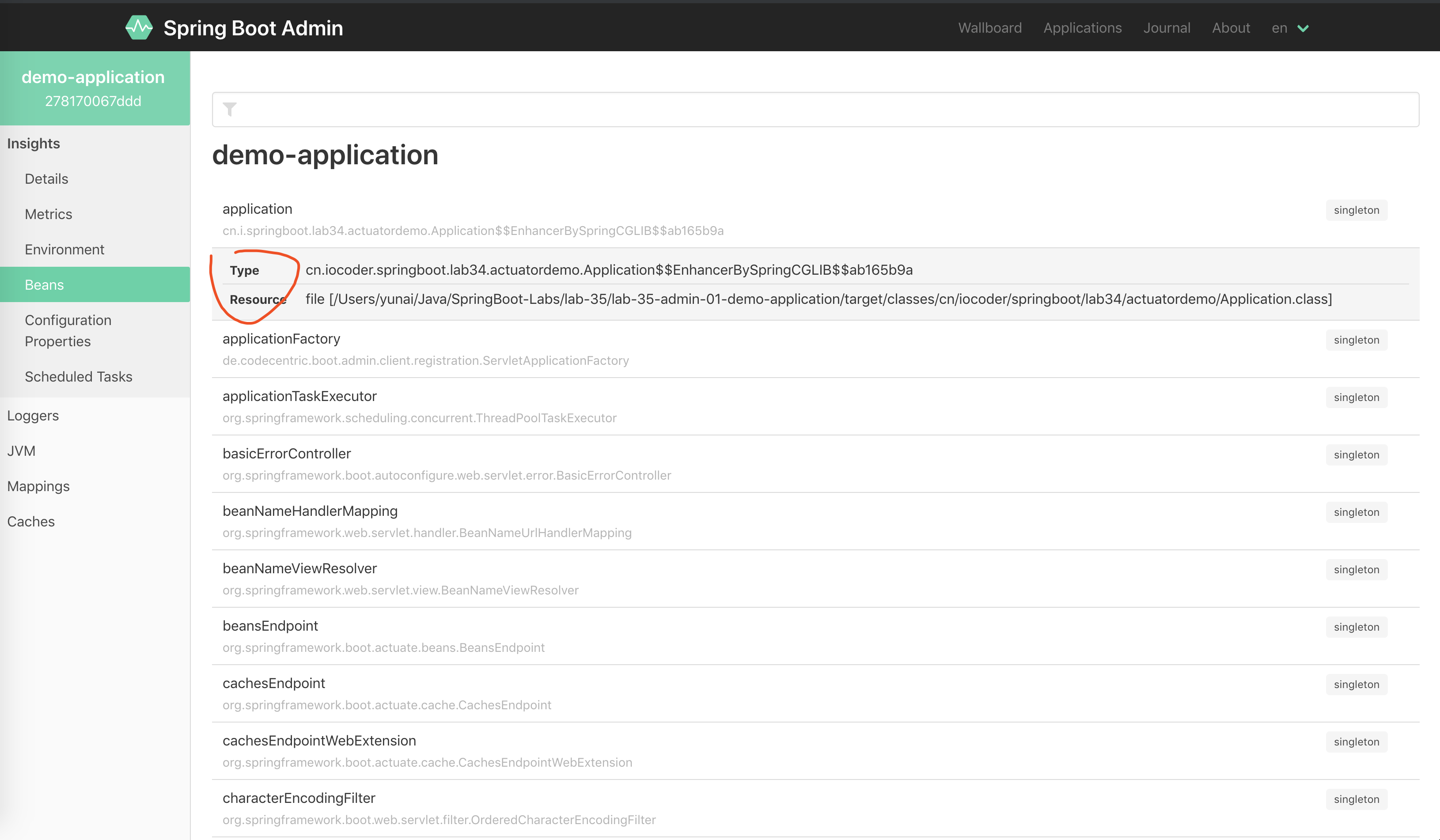
对应 beans 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「9. beans 端点」小节。
3.1.5 Configuration Properties
翻译为配置属性 。如下图:
对应 configprops 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「12. configprops 端点」小节。
3.1.6 Scheduled Tasks
翻译为配置属性 。如下图:
对应 scheduledtasks 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「19. scheduledtasks 端点」小节。
3.2 Loggers
翻译为日志配置 。如下图:
对应 loggers 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「14. loggers 端点」小节。
可以查看和修改 Logger 配置。
3.3 JVM
3.3.1 JMX
翻译为Java 管理扩展 。如下图:
对应《Spring Boot Actuator: Production-ready Features ------ 4. Monitoring and Management over JMX》文档。
3.3.2 Thread Dump
翻译为线程转储 。如下图:
对应 threaddump 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「15. threaddump 端点」小节。
从界面开始,每秒读取一次线程快照。= = 图片上写错了。
3.3.3 Heap Dump
翻译为内存转储 。如下图:
对应 heapdump 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「16. heapdump 端点」小节。
3.4 Mappings
翻译为映射 。如下图:
对应 loggers 端点,可见《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》的「13. mappings 端点」小节。
3.5 Caches
翻译为缓存 。如下图:
对应 caches 端点。
4. 基于 Spring Cloud 注册中心
本小节,我们采用方式二 ,基于 Spring Cloud 支持的注册中心,来实现 Spring Boot Admin 对注册到注册中心的应用,进行监控与管理。这里,我们采用 Eureka 作为注册中心。整个示例的过程如下:
- 首先,我们会创建 lab-35-admin-02-eurekaserver 项目,启动 Eureka Server 注册中心。
- 然后,我们会创建 lab-35-admin-02-demo-application 项目,启动示例项目作为应用,注册到 Eureka Server 上。
- 最后,我们会创建 lab-35-admin-02-adminserver 项目,启动 Spring Boot Admin Server 监控工具。之后,Spring Boot Admin Server 从 Eureka Server 获取到示例项目的两个应用节点,进行监控与管理。
下面,我们会分成三个小小节,分别搭建上述的三个项目。
4.1 Eureka Server
对应 lab-35-admin-02-eurekaserver 项目。
4.1.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-35-admin-02-eurekaserver</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 Eureka Server 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>- 具体每个依赖的作用,胖友自己认真看下艿艿添加的所有注释噢。
4.1.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Eureka Server 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server # 应用名
server:
port: 8761 # 自定义服务器端口,避免冲突
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false # 不注册到 Eureka 中
fetch-registry: false # 不从 Eureka 拉取注册信息- 配置
eureka.client.register-with-eureka = false和eureka.client.fetch-registry = false,避免本地启动的 Eureka Client 注册到自身,以及从自身拉取注册信息。
4.1.3 EurekaServerApplication
创建 EurekaServerApplication 类,启动 Eureka Server。代码如下:
// EurekaServerApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}- 在类上,添加了
@EnableEurekaServer注解,表示开启 Eureka Server 功能。
4.1.4 简单测试
运行 #main(String[] args) 方法,启动 Eureka Server。控制台输出日志如下:
2019-12-28 09:56:03.315 INFO 46583 --- [ Thread-19] e.s.EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration : Started Eureka Server
// ... 省略其它日志- 从日志中,我们可以看到
"Started Eureka Server"。
使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:8761/ 地址,访问 Eureka Server UI。界面如下:
4.2 Eureka Client
对应 lab-35-admin-02-demo-application 项目。
4.2.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-35-admin-02-demo-application</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 Spring MVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Actuator 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Eureka Client 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>- 具体每个依赖的作用,胖友自己认真看下艿艿添加的所有注释噢。
- 相比「2.2 Spring Boot Admin Client」来说,我们通过引入
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client替代spring-boot-admin-starter-client。
4.2.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Eureka Client 配置,如下:
management:
endpoints:
# Actuator HTTP 配置项,对应 WebEndpointProperties 配置类
web:
exposure:
include: '*' # 需要开放的端点。默认值只打开 health 和 info 两个端点。通过设置 * ,可以开放所有端点。
spring:
application:
name: demo-application # 应用名
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka- 配置
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone = http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka,设置 Eureka Server 为我们在「4.1 Eureka Server」所启动的。 - 无需 配置
eureka.client.register-with-eureka和eureka.client.fetch-registry,因为它们默认为true,会使用 Eureka Client 注册到 Eureka Server,以及从 Eureka Server 拉取注册信息。
4.2.3 DemoApplication
创建 Demo01Application 和 Demo02Application 类,用于方便启动该项目的两个应用节点。代码如下:
// Demo01Application.java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class Demo01Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("server.port", "18081"); // 端口 18081
SpringApplication.run(Demo01Application.class, args);
}
}
// Demo02Application.java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class Demo02Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("server.port", "18082"); // 端口 18082
SpringApplication.run(Demo02Application.class, args);
}
}- 在类上,添加了
@EnableDiscoveryClient注解,表示开启 Eureka Client 功能。 - 通过
"server.port"配置项,设置不同的服务器端口。
4.2.4 简单测试
分别 运行 #main(String[] args) 方法,启动该项目的两个应用节点。控制台输出日志如下:
// Demo01Application.java 控制台
2019-12-28 10:17:15.227 INFO 47530 --- [nfoReplicator-0] com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient : DiscoveryClient_DEMO-APPLICATION/192.168.43.240:demo-application:18081 - registration status: 204
// Demo02Application.java 控制台
2019-12-28 10:17:18.502 INFO 47538 --- [nfoReplicator-0] com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient : DiscoveryClient_DEMO-APPLICATION/192.168.43.240:demo-application:18082 - registration status: 204- 从日志中,我们可以看到
"registration",注册到 Eureka Server 成功。
使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:8761/ 地址,访问 Eureka Server UI。界面如下:
- 可以看到
"DEMO-APPLICATION"中,有我们刚启动的两个应用节点,处于 UP 状态。
4.3 Spring Boot Admin Server
对应 lab-35-admin-02-adminserver 项目。
4.3.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-35-admin-02-adminserver</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 Spring Boot Admin Server 的自动化配置 -->
<!--
包含 1. spring-boot-admin-server :Server 端
2. spring-boot-admin-server-ui :UI 界面
3. spring-boot-admin-server-cloud :对 Spring Cloud 的接入
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Eureka Client 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>- 具体每个依赖的作用,胖友自己认真看下艿艿添加的所有注释噢。
- 相比「2.1 Spring Boot Admin Server」来说,我们通过引入
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client,实现从 Eureka Server 拉取注册中心,从而获取到要监控与管理的应用。
4.3.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Eureka Client 配置,如下:
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka
register-with-eureka: false # 不注册到 Eureka 中- 配置
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone = http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka,设置 Eureka Server 为我们在「4.1 Eureka Server」所启动的。 - 配置
eureka.client.register-with-eureka = false,无需使用 Eureka Client 注册到 Eureka Server。😈 我们只要从 Eureka Server 拉取注册信息即可。
4.3.3 AdminServerApplication
创建 AdminServerApplication 类,用于启动 Spring Boot Admin Server。代码如下:
// AdminServerApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAdminServer
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class AdminServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AdminServerApplication.class, args);
}
}- 在类上,添加了
@EnableAdminServer注解,表示开启 Spring Boot Admin Server 功能。 - 在类上,添加了
@EnableDiscoveryClient注解,表示开启 Eureka Client 功能。
4.3.4 简单测试
运行 #main(String[] args) 方法,启动 Spring Boot Admin Server。控制台输出日志如下:
2019-12-28 10:28:44.382 INFO 48006 --- [ main] o.s.b.web.embedded.netty.NettyWebServer : Netty started on port(s): 8080
2019-12-28 10:28:44.383 INFO 48006 --- [ main] .s.c.n.e.s.EurekaAutoServiceRegistration : Updating port to 8080
2019-12-28 10:28:44.387 INFO 48006 --- [ main] c.i.s.l.a.AdminServerApplication : Started AdminServerApplication in 3.637 seconds (JVM running for 4.129)使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:8080/ 地址,访问 Spring Boot Admin Server UI 。界面如下:
- 可以看到
"DEMO-APPLICATION"中,有我们刚启动的两个应用节点,处于在线状态。
后续的使用与测试,参考「3. 功能介绍」即可。
5. Admin Server 安全认证
考虑到安全性,我们需要给 Spring Boot Admin Server 增加安全认证,需要经过登陆之后,才可以使用。
我们可以通过整合 Spring Security 框架,快速的实现安全认证的功能。如果没有学习过 Spring Security 框架的胖友,后续可以看看《芋道 Spring Boot 安全框架 Spring Security 入门》文章。
下面,我们就来进行本小节的示例,考虑到不污染「2. 快速入门」 的示例,我们在 lab-35-admin-01-adminserver 项目的基础上,复制出一个 lab-35-admin-03-adminserver 项目。😈 酱紫,我们也能少写点代码,哈哈哈~
5.1 引入依赖
修改 pom.xml 文件中,额外 引入 spring-boot-starter-security 相关依赖。
<!-- 实现对 Spring Security 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>5.2 SecurityConfig
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab35.adminserver.config 包下,创建 SecurityConfig 配置类,增加 Spring Security 配置。代码如下:
// SecurityConfig.java
@Configuration
@EnableWebFluxSecurity // 开启 Security 对 WebFlux 的安全功能
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public MapReactiveUserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
// 创建一个用户
UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("user")
.password("user")
.roles("USER")
.build();
// 如果胖友有更多用户的诉求,这里可以继续创建
// 创建 MapReactiveUserDetailsService
return new MapReactiveUserDetailsService(user);
}
@Bean
public SecurityWebFilterChain springSecurityFilterChain(ServerHttpSecurity http) {
http.authorizeExchange(exchanges -> // 设置权限配置
exchanges
.pathMatchers("/assets/**").permitAll() // 静态资源,允许匿名访问
.pathMatchers("/login").permitAll() // 登陆接口,允许匿名访问
.anyExchange().authenticated() //
)
.formLogin().loginPage("/login") // 登陆页面
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout") // 登出界面
.and().httpBasic() // HTTP Basic 认证方式
.and().csrf().disable(); // csrf 禁用
return http.build();
}
}- 在类上,添加
@EnableWebFluxSecurity注解,开启 Security 对 WebFlux 的安全功能。😈 因为 Spring Boot Admin Server 是基于 WebFlux 实现的,所以不能按照我们之前针对 Servlet 的配置方式。 #userDetailsService()方法,创建了 MapReactiveUserDetailsService 对象。在其中,我们配置了一个「user/user」账号。如果胖友有更多用户的诉求,这里可以继续创建。#springSecurityFilterChain(...)方法,创建了SecurityWebFilterChain 对象。在其中,我们设置了权限配置、登陆页面、登出地址、禁用 csrf 。
补充说明:
#springSecurityFilterChain(...)方法,我们使用httpBasic()增加了 HTTP Basic 认证方式,主要是为了「6. Admin Client 安全认证」小节中,采用方式一时,Spring Boot Admin Client 可以使用 HTTP Basic 认证方式,进行认证。
5.3 简单测试
运行 #main(String[] args) 方法,启动 Spring Boot Admin Server。控制台输出日志如下:
2019-12-28 12:58:48.539 INFO 52252 --- [ main] o.s.b.web.embedded.netty.NettyWebServer : Netty started on port(s): 8080
2019-12-28 12:58:48.543 INFO 52252 --- [ main] c.i.s.l.a.AdminServerApplication : Started AdminServerApplication in 2.272 seconds (JVM running for 2.895)- 正常启动完成。
使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:8080/ 地址,访问 Spring Boot Admin Server UI 。此时,因为我们暂未登陆,所以被 Spring Security 拦截跳转到 http://127.0.0.1:8080/login 登陆页。如下图:
输入「user/user」账号,完成登陆操作。后续的使用与测试,参考「3. 功能介绍」即可。
6. Admin Client 安全认证
在《芋道 Spring Boot 监控端点 Actuator 入门》中,我们看到可以通过整合 Spring Security 框架,给 Spring Boot Actuator 的端点增加安全认证的功能。这就意味着,如果 Spring Boot Admin Server 访问 Spring Boot Actuator 的端点时,也需要知道该端点的账号密码。
在「2. 快速入门」的方式一 中,我们可以采用 Spring Boot Admin Client 上报 Actuator 端点的账号密码给 Spring Boot Admin Server 。在 application.yml 配置文件中,修改如下即可:
spring.boot.admin.client:
url: http://localhost:8080
instance:
metadata:
user.name: ${spring.security.user.name}
user.password: ${spring.security.user.password}在「4. 基于 Spring Cloud 注册中心」的方式二 中,应用在注册自己到注册中心时,同时在实例的 metadata 元数据中带上 Actuator 端点的账号密码。在 application.yml 配置文件中,修改如下即可:
eureka:
instance:
metadata-map:
user.name: ${spring.security.user.name}
user.password: ${spring.security.user.password}下面,我们就来进行提供下方式一 的示例,考虑到不污染「2. 快速入门」 的示例,我们在 lab-35-admin-01-demo-application 项目的基础上,复制出一个 lab-35-admin-03-demo-application 项目。😈 酱紫,我们也能少写点代码,哈哈哈~
注意,本小节使用的 Spring Boot Admin Server ,对应的是「5. Admin Server 安全认证」小节的 lab-35-admin-03-adminserver 项目。
6.1 引入依赖
修改 pom.xml 文件中,额外 引入 spring-boot-starter-security 相关依赖。
<!-- 实现对 Spring Security 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>6.2 配置文件
修改 application.yml 配置文件,添加安全认证所需的配置,如下:
management:
endpoints:
# Actuator HTTP 配置项,对应 WebEndpointProperties 配置类
web:
exposure:
include: '*' # 需要开放的端点。默认值只打开 health 和 info 两个端点。通过设置 * ,可以开放所有端点。
spring:
application:
name: demo-application # 应用名
# Spring Security 配置项,对应 SecurityProperties 配置类
security:
# 配置默认的 InMemoryUserDetailsManager 的用户账号与密码。
user:
name: test # 账号
password: test # 密码
boot:
admin:
client:
url: http://127.0.0.1:8080 # Spring Boot Admin Server 地址
username: user # Spring Boot Admin Server 的认证账号
password: user # Spring Boot Admin Server 的认证密码
instance:
metadata:
user.name: ${spring.security.user.name} # Actuator 端点的认证账号
user.password: ${spring.security.user.password} # Actuator 端点的认证密码
server:
port: 18080 # 设置自定义 Server 端口,避免和 Spring Boot Admin Server 端口冲突。- 我们结合「2.2.2 配置文件」小节,来说说新增的三个配置。
- 第一点,新增
spring.security.user配置项,配置了一个 Spring Security 认证账号。后续 Spring Boot Admin Server 在访问该应用的 Actuator 的端点时,需要使用该账号进行认证。 - 第二点,新增
spring.boot.admin.client.instance.metadata配置项,设置 Actuator 端点的认证账号和密码。 - 第三点,因为「5. Admin Server 安全认证」小节的 Spring Boot Server Admin 开启了安全认证,所以,我们在
spring.boot.admin.client配置项下,额外配置了username和password,值为 Spring Boot Admin Server 的认证账号和密码。
6.3 简单测试
运行 #main(String[] args) 方法,启动示例项目。控制台输出日志如下:
2019-12-28 13:35:29.281 INFO 53866 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 18080 (http) with context path ''
2019-12-28 13:35:29.284 INFO 53866 --- [ main] c.i.s.lab35.demo.DemoApplication : Started DemoApplication in 2.172 seconds (JVM running for 2.632)
2019-12-24 13:35:29.460 INFO 53866 --- [1)-192.168.3.44] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring DispatcherServlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2019-12-28 13:35:29.460 INFO 53866 --- [1)-192.168.3.44] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet 'dispatcherServlet'
2019-12-28 13:35:29.464 INFO 53866 --- [1)-192.168.3.44] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 4 ms
2019-12-28 13:35:29.681 INFO 53866 --- [gistrationTask1] d.c.b.a.c.r.ApplicationRegistrator : Application registered itself as 278170067ddd- 重点看到最后一行日志,示例项目成功注册到 Spring Boot Admin Server 上。
后续的使用与测试,胖友可以自己在 Spring Boot Admin Server UI 界面上,自己愉快的玩耍。
7. 监控告警
在 Spring Boot Admin 中,已经集成告警功能。例如说,被监控的应用状态变更为 DOWN、OFFLINE、UNKNOWN 时,会自动发出告警。
Spring Boot Admin 内置了多种告警方式:
- Mail Notifications 邮件告警
- PagerDuty Notifications
- OpsGenie Notifications
- Hipchat Notifications
- Slack Notifications
- Let's Chat Notifications
- Microsoft Teams Notifications
- Telegram Notifications
- Discord Notifications
考虑到可能告警胖友会漏看,或者不及时,Spring Boot Admin 支持针对 DOWN、OFFLINE 的应用的重复告警 。具体的,可以参考《Spring Boot Admin Reference Guide ------ 4.5.11. Notification Reminder》文档。
考虑到并不是所有告警通知都是我们所需要的,Spring Boot Admin 提供了过滤机制 。具体的,可以参考《Spring Boot Admin Reference Guide ------ 4.5.12. Filtering Notifications》文档。
7.1 邮件告警
考虑到基于邮件,是我们最常用 的告警方式,所以在本小节中,我们来搭建一个 Spring Boot Admin 邮件告警的示例。考虑到不污染「2. 快速入门」 的示例,我们在 lab-35-admin-01-adminserver 项目的基础上,复制出一个 lab-35-admin-04-adminserver 项目。😈 酱紫,我们也能少写点代码,哈哈哈~
注意,本小节使用的 Spring Boot Admin Client ,对应的是「2.2 Spring Boot Admin Client」小节的 lab-35-admin-01-demo-application 项目。
7.1.1 引入依赖
修改 pom.xml 文件中,额外 引入 spring-boot-starter-mail 相关依赖。
<!-- 实现对 Java Mail 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>7.1.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加邮件告警的配置,如下:
spring:
mail: # 配置发送告警的邮箱
host: smtp.126.com
username: wwbmlhh@126.com
password: '******'
default-encoding: UTF-8
boot:
admin:
notify:
mail:
from: ${spring.mail.username} # 告警发件人
to: 7685413@qq.com # 告警收件人- 在
spring.mail配置项下,设置发送告警的邮箱。 - 在
spring.boot.admin.nofity.mail配置项下,设置 Spring Boot Admin Server 邮件告警的配置。
7.1.3 简单测试
首先,我们使用 lab-35-admin-04-adminserver 项目,启动一个 Spring Boot Admin Server 。
然后,我们使用 lab-35-admin-01-demo-application 项目,启动一个被监控的应用,采用方式一 Spring Boot Admin Client ,成功注册到上述的 Spring Boot Admin Server 上。
之后,我们主动 关闭被监控的应用,模拟应用下线的场景 ,从而触发告警。此时,我们打开接收告警的邮箱,成功收到一封告警邮件。如下图:
7.2 自定义告警
虽然说,Spring Boot Admin 已经内置了多种告警方式,但是实际场景下,我们可能还需要其它告警方式。例如说,短信告警、电话告警、钉钉告警、公众号告警等等。
下面,我们来搭建一个 Spring Boot Admin 自定义告警的示例。考虑到不污染「2. 快速入门」 的示例,我们在 lab-35-admin-01-adminserver 项目的基础上,复制出一个 lab-35-admin-05-adminserver 项目。😈 酱紫,我们也能少写点代码,哈哈哈~
注意,本小节使用的 Spring Boot Admin Client ,对应的是「2.2 Spring Boot Admin Client」小节的 lab-35-admin-01-demo-application 项目。
7.2.1 LoggerNotifier
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab35.adminserver.notify 包下,创建 LoggerNotifier 类,实现 AbstractEventNotifier 抽象类,实现自定义告警。代码如下:
// LoggerNotifier.java
@Component
public class LoggerNotifier extends AbstractStatusChangeNotifier {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
public LoggerNotifier(InstanceRepository repository) {
super(repository);
}
@Override
protected Mono<Void> doNotify(InstanceEvent event, Instance instance) {
return Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
if (event instanceof InstanceStatusChangedEvent) {
logger.info("Instance {} ({}) is {}", instance.getRegistration().getName(), event.getInstance(),
((InstanceStatusChangedEvent) event).getStatusInfo().getStatus());
} else {
logger.info("Instance {} ({}) {}", instance.getRegistration().getName(), event.getInstance(), event.getType());
}
});
}
}- AbstractEventNotifier 是 Spring Boot Admin 定义的事件通知器的抽象基类 ,其类图如下:

- InstanceEvent 是 Spring Boot Admin 定义的实例事件的抽象基类 ,其类图如下:

- 通过实现
#doNotify(InstanceEvent event, Instance instance)方法,实现对指定实例的指定事件,进行自定义的告警通知。例如说,调用短信发送接口、钉钉消息发送接口等等。这里,😈 我们为了简单化,就打印下日志吧,嘿嘿。
7.2.2 简单测试
首先,我们使用 lab-35-admin-05-adminserver 项目,启动一个 Spring Boot Admin Server 。
然后,我们使用 lab-35-admin-01-demo-application 项目,启动一个被监控的应用,采用方式一 Spring Boot Admin Client ,成功注册到上述的 Spring Boot Admin Server 上。此时,Spring Boot Admin Server 控制台输出日志如下:
# 非 InstanceStatusChangedEvent 事件
2019-12-28 16:00:24.268 INFO 58652 --- [ctor-http-nio-2] c.i.s.l.a.notify.LoggerNotifier : Instance demo-application (278170067ddd) REGISTERED
2019-12-28 16:00:24.393 INFO 58652 --- [ctor-http-nio-3] c.i.s.l.a.notify.LoggerNotifier : Instance demo-application (278170067ddd) is UP
2019-12-28 16:00:24.434 INFO 58652 --- [ctor-http-nio-3] c.i.s.l.a.notify.LoggerNotifier : Instance demo-application (278170067ddd) ENDPOINTS_DETECTED之后,我们主动 关闭被监控的应用,模拟应用下线的场景,从而触发告警。此时,Spring Boot Admin Server 控制台输出日志如下:
# InstanceStatusChangedEvent 事件
2019-12-28 16:02:21.673 INFO 58652 --- [ctor-http-nio-3] c.i.s.l.a.notify.LoggerNotifier : Instance demo-application (278170067ddd) is OFFLINE一般来说,我们只基于 InstanceStatusChangedEvent 事件,进行告警处理。例如说,MailNotifier 邮件通知器,通过继承 AbstractStatusChangeNotifier 抽象类,只处理 InstanceStatusChangedEvent 实例状态变化事件,进行发送邮件。
7.3 钉钉告警
基于「7.2 自定义告警」的方式,我们可以实现钉钉告警。
代码比较简单,胖友可以直接参考 https://github.com/luoyoubao/springboot-admin-demo 仓库。艿艿偷个小懒,嘿嘿。
至此,我们已经完成了 Spring Boot Admin 的学习。总得来说,Spring Boot Admin 算是不错的轻量级的监控工具,只需要极少量的配置,就可以完成 Spring Boot 的应用的监控、管理、甚至说告警。一般情况下,如果想要快速搭建一个监控工具,那么 Spring Boot Admin 算是一个不错的选择。
不过呢,Spring Boot Admin 比较大的一个问题,并不会主动 采集 Spring Boot 应用的 Metrics 指标数据,记录到存储器中。这样就会导致,我们如果排查问题时,需要查看过去一段时间的 Metrics 指标数据,就无从得知。当然,此时我们可以考虑通过 Prometheus + Grafana 打造监控平台 。😈 感兴趣的胖友,可以阅读《Spring Boot 监控平台 Prometheus + Grafana 入门》文章。
更多的时候,我们可以把 Spring Boot Admin 看成 Spring Boot 应用的 Actuator 的网关 ,负责将 UI 界面需要的数据,转发到对应的应用的 Actuator 的端点,从而让我们可以进行不同应用实例的监控与管理。也因此,艿艿把 Spring Boot Admin 定义为监控工具。
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42073629/article/details/106771727