58.Spring Boot 链路追踪 Zipkin 入门
58.Spring Boot 链路追踪 Zipkin 入门
1. 概述
如果胖友还没了解过分布式链路追踪 Zipkin,建议先阅读下艿艿写的 《Zipkin 极简入门》 文章。虽然这篇文章标题是安装部署,实际可以理解成《一文带你快速入门 Zipkin》,哈哈哈。
可能会有胖友会有疑惑,Spring Boot 不是一个单体应用么,为什么可以使用 Zipkin 进行分布式链路追踪呢?其实这里有一个误区!即使是一个 Spring Boot 单体应用,我们一般可能会和以下服务打交道:
- 关系数据库,例如说 MySQL、Oracle、SQLServer、PostgreSQL 等等。
- 文档数据库,例如说 MongoDB 等等。
- 缓存数据库,例如说 Redis、Memcached 等等。
- 外部三方服务,例如说微信公众号、微信支付、支付宝支付、短信平台等等。
那么即使是一个 Spring Boot 单体应用,就已经涉及到分布在不同进程 中的服务。此时,就已经满足使用 Zipkin 进行分布式链路追踪的条件,同时也是非常有必要的。例如说,我们线上某个 API 接口访问非常慢,可以通过 Zipkin 来排查,是因为 MySQL 查询比较慢呢,还是调用的第三方服务比较慢。
在本文中,我们会比《Zipkin 极简入门》提供更多在 Spring Boot 中使用的示例。例如说:
- 对 SpringMVC 的 API 接口的链路追踪
- 对 JDBC 访问 MySQL 的链路追踪
- 对 Jedis 访问 Redis 的链路追踪
- 对 RabbitMQ 的消息的发送和消费的链路追踪
- 等等等等
2. SpringMVC 示例
示例代码对应仓库:
labx-13-sc-sleuth-springmvc。
本小节,我们来搭建一个 Zipkin 对 SpringMVC 的 API 接口的链路追踪。该链路通过如下插件实现收集:
友情提示:一般来说,在 Java 应用程序中,我们使用 Brave 库,作为 Zipkin Server 的 Java Tracer 客户端。同时它的 instrumentation 子项目,已经提供了 SpringMVC、MySQL、Dubbo 等等的链路追踪的功能。
本文对 instrumentation 统称为"插件"。
2.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-springmvc</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>2.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加应用名配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-springmvc- 该应用名,稍后也会作为 Zipkin 链路追踪的本地应用名。
2.3 配置类
① cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.configuration 包路径下,创建 ZipkinConfiguration 配置类,配置 Zipkin 链路追踪相关的 Bean。代码如下:
@Configuration
public class ZipkinConfiguration {
// ==================== 通用配置 ====================
/**
* Configuration for how to send spans to Zipkin
*/
@Bean
public Sender sender() { // Sender 采用 HTTP 通信方式
return OkHttpSender.create("http://127.0.0.1:9411/api/v2/spans");
}
/**
* Configuration for how to buffer spans into messages for Zipkin
*/
@Bean
public AsyncReporter<Span> spanReporter() { // 异步 Reporter
return AsyncReporter.create(sender());
}
/**
* Controls aspects of tracing such as the service name that shows up in the UI
*/
@Bean
public Tracing tracing(@Value("${spring.application.name}") String serviceName) {
return Tracing.newBuilder()
.localServiceName(serviceName) // 应用名
.spanReporter(this.spanReporter()).build();
}
/**
* Allows someone to add tags to a span if a trace is in progress
*/
@Bean
public SpanCustomizer spanCustomizer(Tracing tracing) {
return CurrentSpanCustomizer.create(tracing);
}
// ==================== HTTP 相关 ====================
/**
* Decides how to name and tag spans. By default they are named the same as the http method
*/
@Bean
public HttpTracing httpTracing(Tracing tracing) {
return HttpTracing.create(tracing);
}
/**
* Creates server spans for http requests
*/
@Bean
public Filter tracingFilter(HttpTracing httpTracing) { // 拦截请求,记录 HTTP 请求的链路信息
return TracingFilter.create(httpTracing);
}
// ==================== SpringMVC 相关 ====================
// @see SpringMvcConfiguration 类上的,@Import(SpanCustomizingAsyncHandlerInterceptor.class) 。因为 SpanCustomizingAsyncHandlerInterceptor 未提供 public 构造方法
}- 配置的 Bean 比较多,胖友结合中文和英语注释,还是很容易理解的。同时,注意下
===分割线做的大类拆分。
② 在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.configuration 包路径下,创建 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类,配置 Zipkin 拦截器。代码如下:
@Configuration
@Import(SpanCustomizingAsyncHandlerInterceptor.class) // 创建拦截器 SpanCustomizingAsyncHandlerInterceptor Bean
public class SpringMvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
public SpanCustomizingAsyncHandlerInterceptor webMvcTracingCustomizer;
/**
* Decorates server spans with application-defined web tags
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // 记录 SpringMVC 相关信息到 Span 中
registry.addInterceptor(webMvcTracingCustomizer);
}
}2.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("/springmvc")
public String echo() {
return "springmvc";
}
}2.5 SpringMVCApplication
创建 SpringMVCApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringMVCApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringMVCApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 SpringMVCApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
2.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/springmvc 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击第一个 Span,可以看到一个 Span 明细。如下图所示:
3. MySQL 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-mysql。
本小节,我们来搭建一个 Zipkin 对 MySQL 操作的链路追踪。该链路通过如下插件实现收集:
我们将使用 Spring JdbcTemplate 进行 MySQL 的操作。对 Spring JdbcTemplate 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《Spring Boot JdbcTemplate 入门》文章。
3.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-mysql</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对数据库连接池的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency> <!-- 本示例,我们使用 MySQL -->
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.46</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 MySQL 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-mysql</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 具体每个依赖的作用,胖友自己认真看下艿艿添加的所有注释噢。
- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-instrumentation-mysql依赖。
3.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加数据库相关配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-mysql
# datasource 数据源配置内容
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/lab-39-mysql?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&statementInterceptors=brave.mysql.TracingStatementInterceptor&zipkinServiceName=demo-db-mysql
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password:- 通过自定义 StatementInterceptorV2 的实现类 TracingStatementInterceptor,达到拦截 SQL 请求,进行 MySQL 的链路追踪。
- 在
spring.datasource.url配置项上的statementInterceptors和zipkinServiceName属性,分别设置拦截器和该 MySQL 在 Zipkin 中展示的服务名。
这里,胖友记得在测试的数据库中,创建 t_user 表,并插入一条 id = 1 的记录。SQL 脚本如下:
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int(8) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键自增',
`username` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`password` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '密码',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='用户表';
INSERT INTO `t_user`(`id`, `username`, `password`) VALUES (1, 'yudaoyuanma', 'nicai');3.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。
3.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate template;
@GetMapping("/mysql")
public String echo() {
this.selectById(1);
return "mysql";
}
public Object selectById(Integer id) {
return template.queryForObject("SELECT id, username, password FROM t_user WHERE id = ?",
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Object.class), // 结果转换成对应的对象。Object 理论来说是 UserDO.class ,这里偷懒了。
id);
}
}- 在
/demo/mysql接口中,会执行一次 MySQL 的查询。
3.5 MySQLApplication
创建 MySQLApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySQLApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}执行 MySQLApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
3.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/mysql 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示: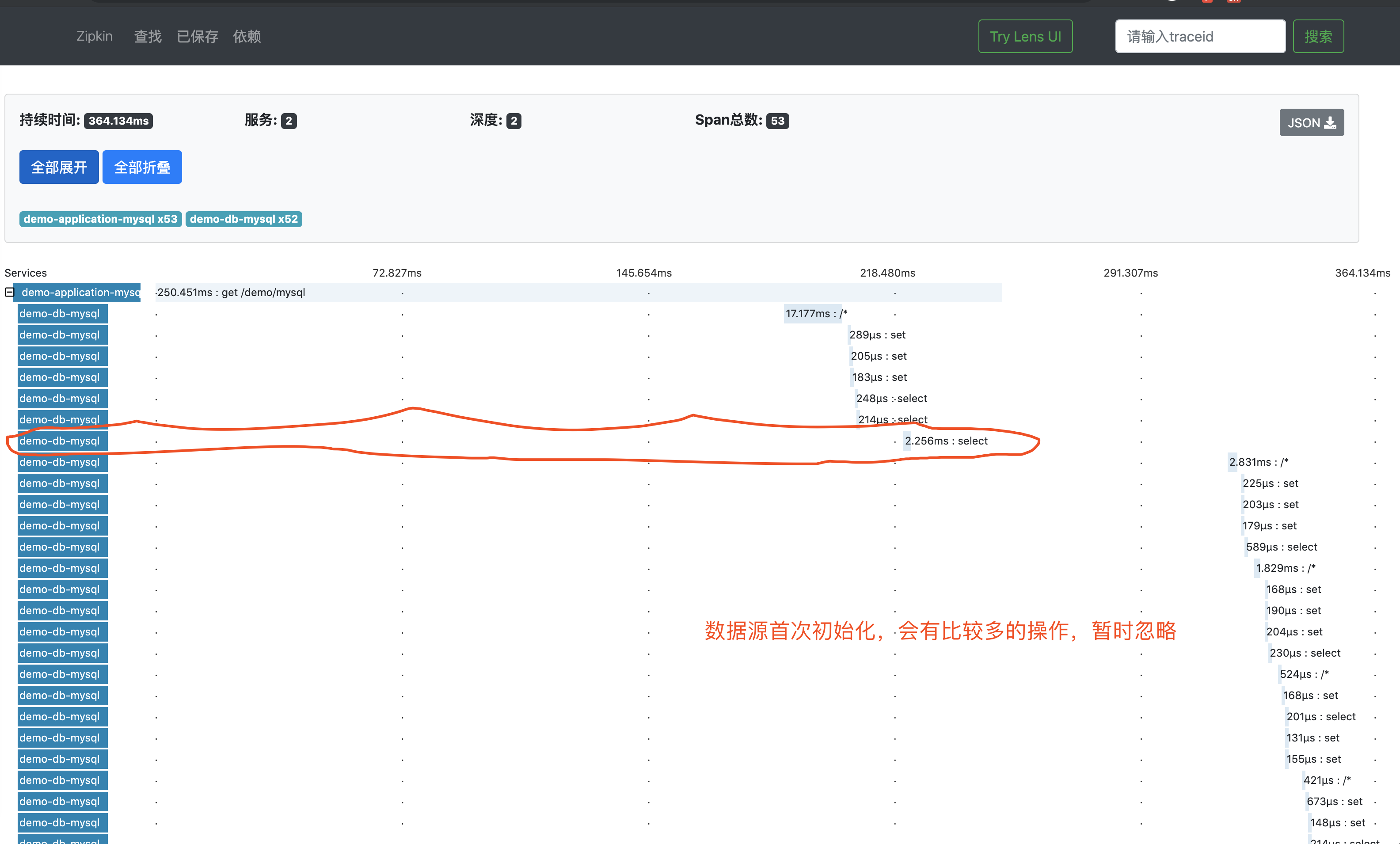
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Span 明细。如下图所示:
4. Redis 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-redis。
本小节,我们来搭建一个 Zipkin 对 Redis 操作的链路追踪。Brave 并未提供对 Jedis、Lettuce、Redisson 等等 Redis 客户端的支持,所以我们只能另寻途径。
在 opentracing-contrib 项目中,有一个 java-redis-client 子项目,提供了 OpenTracing 针对 Jedis、Lettuce、Redisson 等等客户端的链路追踪。这样,我们搭配上 brave-opentracing 项目,就可以将使用 OpenTracing API 收集的链路数据,发送给 Zipkin Server 中。
brave-opentracing:OpenTracing Java Bridge for Zipkin。
This library is a Java bridge between the Brave/Zipkin Api and OpenTracing. It allows its users to write portable (in the OpenTracing sense) instrumentation that's translated into Brave instrumentation transparently.
我们将使用 Spring Data Redis + Jedis 进行 Redis 的操作。对 Spring Data Redis 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《Spring Boot Redis 入门》文章。
4.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-redis</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Spring Data Redis 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<!-- 去掉对 Lettuce 的依赖,因为 Spring Boot 优先使用 Lettuce 作为 Redis 客户端 -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入 Jedis 的依赖,这样 Spring Boot 实现对 Jedis 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 Opentracing 的实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-opentracing</artifactId>
<version>0.35.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Opentracing 对 Redis 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.contrib</groupId>
<artifactId>opentracing-redis-jedis3</artifactId>
<version>0.1.14</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.contrib</groupId>
<artifactId>opentracing-redis-spring-data</artifactId>
<version>0.1.14</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 具体每个依赖的作用,胖友自己认真看下艿艿添加的所有注释噢。
- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-brave-opentracing和opentracing-redis-spring-data+opentracing-redis-jedis3依赖。
4.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Redis 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-redis
# 对应 RedisProperties 类
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password: # Redis 服务器密码,默认为空。生产中,一定要设置 Redis 密码!
database: 0 # Redis 数据库号,默认为 0 。
timeout: 0 # Redis 连接超时时间,单位:毫秒。
# 对应 RedisProperties.Jedis 内部类
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 8 # 连接池最大连接数,默认为 8 。使用负数表示没有限制。
max-idle: 8 # 默认连接数最小空闲的连接数,默认为 8 。使用负数表示没有限制。
min-idle: 0 # 默认连接池最小空闲的连接数,默认为 0 。允许设置 0 和 正数。
max-wait: -1 # 连接池最大阻塞等待时间,单位:毫秒。默认为 -1 ,表示不限制。4.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,额外增加了如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
// ==================== 通用配置 ====================
@Bean
public Tracer openTracer(Tracing tracing) {
return BraveTracer.create(tracing);
}
// ==================== Redis 相关 ====================
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory(Tracer tracer, RedisProperties redisProperties) {
// 创建 JedisConnectionFactory 对象
RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory();
// 创建 TracingConfiguration 对象
TracingConfiguration tracingConfiguration = new TracingConfiguration.Builder(tracer)
// 设置拓展 Tag ,设置 Redis 服务器地址。因为默认情况下,不会在操作 Redis 链路的 Span 上记录 Redis 服务器的地址,所以这里需要设置。
.extensionTag("Server Address", redisProperties.getHost() + ":" + redisProperties.getPort())
.build();
// 创建 TracingRedisConnectionFactory 对象
return new TracingRedisConnectionFactory(connectionFactory, tracingConfiguration);
}#openTracer()方法,创建一个 BraveTracer Bean 对象。BraveTracer 是 Opentracing Tracer 接口的实现类。#redisConnectionFactory(...)方法,创建一个 TracingRedisConnectionFactory Bean 对象。这样,我们就能拦截到 Redis 操作,进行 Redis 的链路追踪。
4.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/redis")
public String redis() {
this.get("demo");
return "redis";
}
public void get(String key) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
}
}- 在
/demo/redis接口中,会执行一次 Redis 的查询。
4.5 RedisApplication
创建 RedisApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class RedisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RedisApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 RedisApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
4.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/redis 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Span 明细。如下图所示:
5. MongoDB 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-mongodb。
和「4. Redis 示例」一样,Brave 并未提供对 对 MongoDB 操作的链路追踪。因此,我们还是使用 opentracing-contrib 的子项目 java-mongo-driver,搭配上 brave-opentracing 项目,实现将使用 OpenTracing API 收集的链路数据,发送给 Zipkin Server 中。
我们将使用 Spring Data MongoDB 进行 MongoDB 的操作。对 Spring Data MongoDB 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《芋道 Spring Boot MongoDB 入门》文章。
5.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-mongodb</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 自动化配置 Spring Data Mongodb -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 Opentracing 的实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-opentracing</artifactId>
<version>0.35.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Opentracing 对 MongoDB 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.contrib</groupId>
<artifactId>opentracing-mongo-driver</artifactId>
<version>0.1.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 具体每个依赖的作用,胖友自己认真看下艿艿添加的所有注释噢。
- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-brave-opentracing和opentracing-mongo-driver依赖。
5.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 MongoDB 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: dmeo-application-mongodb
data:
# MongoDB 配置项,对应 MongoProperties 类
mongodb:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 27017
database: yourdatabase
username: test01
password: password01
# 上述属性,也可以只配置 uri5.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,额外增加了如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
// ==================== 通用配置 ====================
@Bean
public Tracer openTracer(Tracing tracing) {
return BraveTracer.create(tracing);
}
// ==================== MongoDB 相关 ====================
@Bean
public MongoClientOptions mongoClientOptions(Tracer tracer) {
// 创建 TracingCommandListener 对象
TracingCommandListener listener = new TracingCommandListener.Builder(tracer).build();
// 创建 MongoClientOptions 对象,并设置监听器
return MongoClientOptions.builder().addCommandListener(listener).build();
}#openTracer()方法,创建一个 BraveTracer Bean 对象。BraveTracer 是 Opentracing Tracer 接口的实现类。#mongoClientOptions(...)方法,创建一个带有 TracingCommandListener 监听器的 MongoClientOptions Bean 对象。这样,我们就能拦截到 MongoDB 操作,进行 MongoDB 的链路追踪。
5.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@GetMapping("/mongodb")
public String mysql() {
this.findById(1);
return "mongodb";
}
public UserDO findById(Integer id) {
return mongoTemplate.findOne(new Query(Criteria.where("_id").is(id)), UserDO.class);
}
}- 在
/demo/mongodb接口中,会执行一次 MongoDB 查询操作。 - UserDO 实体类,直接点击查看。
5.5 MongoDBApplication
创建 MongoDBApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MongoDBApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MongoDBApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 MongoDBApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
5.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/mongodb 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Span 明细。如下图所示:
6. Elasticsearch 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-elasticsearch。
和「4. Redis 示例」一样,Brave 并未提供对 对 Elasticsearch 操作的链路追踪。因此,我们还是使用 opentracing-contrib 的子项目 java-elasticsearch-client,搭配上 brave-opentracing 项目,实现将使用 OpenTracing API 收集的链路数据,发送给 Zipkin Server 中。
我们将使用 Spring Data Elasticsearch 进行 Elasticsearch 的操作。对 Elasticsearch 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《Spring Boot Elasticsearch 入门》文章。
6.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-elasticsearch</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 自动化配置 Spring Data Elasticsearch -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 Opentracing 的实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-opentracing</artifactId>
<version>0.35.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Opentracing 对 Elasticsearch 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.contrib</groupId>
<artifactId>opentracing-elasticsearch6-client</artifactId>
<version>0.1.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-brave-opentracing和opentracing-elasticsearch6-client依赖。
6.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 MongoDB 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-elasticsearch
data:
# Elasticsearch 配置项
elasticsearch:
cluster-name: elasticsearch # 集群名
cluster-nodes: 127.0.0.1:9300 # 集群节点6.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,额外增加了如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
// ==================== 通用配置 ====================
@Bean
public Tracer openTracer(Tracing tracing) {
return BraveTracer.create(tracing);
}
// ==================== Elasticsearch 相关 ====================
@Bean
public TransportClient elasticsearchClient(Tracer tracer, ElasticsearchProperties elasticsearchProperties) throws Exception {
// 创建 TracingTransportClientFactoryBean 对象
TracingTransportClientFactoryBean factory = new TracingTransportClientFactoryBean(tracer);
// 设置其属性
factory.setClusterNodes(elasticsearchProperties.getClusterNodes());
factory.setProperties(this.createElasticsearch(elasticsearchProperties));
// 创建 TransportClient 对象,并返回
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
private Properties createElasticsearch(ElasticsearchProperties elasticsearchProperties) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("cluster.name", elasticsearchProperties.getClusterName());
properties.putAll(elasticsearchProperties.getProperties());
return properties;
}#openTracer()方法,创建一个 BraveTracer Bean 对象。BraveTracer 是 Opentracing Tracer 接口的实现类。#elasticsearchClient(...)方法,先创建一个 TracingTransportClientFactoryBean 对象,之后通过它创建可追踪链路的 TracingPreBuiltTransportClient Bean 对象。这样,我们就能拦截到 Elasticsearch 操作,进行 Elasticsearch 的链路追踪。
不过因为 opentracing-elasticsearch6-client 提供的 TracingPreBuiltTransportClient 类,是直接继承 PreBuiltTransportClient 类,并且并未提供传入 PreBuiltTransportClient 参数的构造方法,导致我们不能通过直接修饰 TransportClient Bean 的方式,而是只能自己定义了一个 TracingTransportClientFactoryBean 类,创建可追踪链路的 TracingPreBuiltTransportClient 对象。
TracingTransportClientFactoryBean 基本复制 TransportClientFactoryBean 的代码,主要重写了 #buildClient() 方法,创建 TracingPreBuiltTransportClient 对象。代码如下:
// TracingTransportClientFactoryBean.java
private Tracer tracer;
protected void buildClient() throws Exception {
// 创建可追踪的 TracingPreBuiltTransportClient
client = new TracingPreBuiltTransportClient(tracer, settings());
// ... 省略其它代码
}可能这么说略微有点晦涩,胖友先继续往下看,等后面自己动手实践一次,就会很好理解了。
6.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private ESUserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping("/elasticsearch")
public String mysql() {
this.findById(1);
return "elasticsearch";
}
public ESUserDO findById(Integer id) {
return userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
}- 在
/demo/elasticsearch接口中,会执行一次 Elasticsearch 插入和查询操作。 - ESUserDO 实体类,直接点击查看。
- ESUserRepository ES 数据访问类,直接点击查看。
6.5 ElasticsearchJestApplication
创建 ElasticsearchJestApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration.class, ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration.class})
public class ElasticsearchJestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ElasticsearchJestApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 ElasticsearchJestApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
6.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/mongodb 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Span 明细。如下图所示:
7. RocketMQ 示例
比较遗憾,我们暂时无法在 Zipkin 中,实现对 RocketMQ 的链路追踪。原因如下:
- Brave 暂时没有提供 RocketMQ 的链路追中的插件。
- OpenTracing API Contributions 也没提供对 RocketMQ 的链路追中的插件。
- RocketMQ 自身也并未提供对 OpenTracing 的集成。相关讨论,可见 ISSUE#1525。
如果胖友想要实现对 RocketMQ 的链路追踪,可以考虑下 SkyWalking。详细可见《芋道 Spring Boot 链路追踪 SkyWalking 入门》的「8. RocketMQ 示例」小节。
8. Kafka 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-kafka。
本小节,我们来搭建一个 Zipkin 对 Kafka 消息的发送和消费的链路追踪。该链路通过如下插件实现收集:
brave-instrumentation-messagingbrave-instrumentation-kafka-clientsbrave-instrumentation-kafka-streams
我们将使用 Spring-Kafka 进行 Kafka 的操作。对 Kafka 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《芋道 Spring Boot 消息队列 Kafka 入门》文章。
考虑到让示例更简单,我们的示例项目包含 Kafka 的生产者 Producer 和消费者 Consumer。
8.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.11.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-kafka</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入 Spring-Kafka 依赖 -->
<!-- 已经内置 kafka-clients 依赖,所以无需重复引入 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
<version>2.2.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 Kafka 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-kafka-clients</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-instrumentation-kafka-clients依赖。
8.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Kafka 配置,如下:
server:
port: 8079
spring:
# Kafka 配置项,对应 KafkaProperties 配置类
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: 127.0.0.1:9092 # 指定 Kafka Broker 地址,可以设置多个,以逗号分隔
# Kafka Producer 配置项
producer:
acks: 1 # 0-不应答。1-leader 应答。all-所有 leader 和 follower 应答。
retries: 3 # 发送失败时,重试发送的次数
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer # 消息的 key 的序列化
value-serializer: org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonSerializer # 消息的 value 的序列化
# Kafka Consumer 配置项
consumer:
auto-offset-reset: earliest # 设置消费者分组最初的消费进度为 earliest 。可参考博客 https://blog.csdn.net/lishuangzhe7047/article/details/74530417 理解
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonDeserializer
properties:
spring:
json:
trusted:
packages: cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.message # 消息 POJO 可信目录,解决 JSON 无法反序列化的问题
# Kafka Consumer Listener 监听器配置
listener:
missing-topics-fatal: false # 消费监听接口监听的主题不存在时,默认会报错。所以通过设置为 false ,解决报错8.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,额外增加了如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
// ==================== Kafka 相关 ====================
@Bean
public KafkaTracing kafkaTracing(Tracing tracing) {
return KafkaTracing.newBuilder(tracing)
.remoteServiceName("demo-mq-kafka") // 远程 Kafka 服务名,可自定义
.build();
}
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<?, ?> kafkaProducerFactory(KafkaProperties properties, KafkaTracing kafkaTracing) {
// 创建 DefaultKafkaProducerFactory 对象
DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<?, ?> factory = new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory(properties.buildProducerProperties()) {
@Override
public Producer createProducer() {
// 创建默认的 Producer
Producer<?, ?> producer = super.createProducer();
// <X> 创建可链路追踪的 Producer
return kafkaTracing.producer(producer);
}
};
// 设置事务前缀
String transactionIdPrefix = properties.getProducer().getTransactionIdPrefix();
if (transactionIdPrefix != null) {
factory.setTransactionIdPrefix(transactionIdPrefix);
}
return factory;
}
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<?, ?> kafkaConsumerFactory(KafkaProperties properties, KafkaTracing kafkaTracing) {
// 创建 DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory 对象
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory(properties.buildConsumerProperties()) {
@Override
public Consumer<?, ?> createConsumer(String groupId, String clientIdPrefix, String clientIdSuffix) {
return this.createConsumer(groupId, clientIdPrefix, clientIdSuffix, null);
}
@Override
public Consumer<?, ?> createConsumer(String groupId, String clientIdPrefix, final String clientIdSuffixArg, Properties properties) {
// 创建默认的 Consumer
Consumer<?, ?> consumer = super.createConsumer(groupId, clientIdPrefix, clientIdSuffixArg, properties);
// <Y> 创建可链路追踪的 Consumer
return kafkaTracing.consumer(consumer);
}
};
}#kafkaTracing(...)方法,创建 KafkaTracing Bean。#kafkaProducerFactory(...)方法,创建 ProducerFactory Bean 对象。重点在<X>处,创建可链路追踪的 Kafka Producer 对象。#kafkaConsumerFactory(...)方法,创建 ConsumerFactory Bean 对象。重点在<Y>处,创建可链路追踪的 Kafka Consumer 对象。- 另外,如果胖友有采集率的需求,可以看看《Brave Kafka instrumentation ------ Sampling Policy》文档。
8.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private DemoProducer producer;
@GetMapping("/kafka")
public String echo() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
this.sendMessage(1);
return "kafka";
}
public void sendMessage(Integer id) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
producer.syncSend(id);
}
}- 在
/demo/kafka接口中,会执行一次 Kafka 发送消息的操作。 - DemoMessage 消息类,直接点击查看。
- DemoProducer 生产者类,直接点击查看。
- DemoConsumer 消费者类,直接点击查看。
8.5 KafkaApplication
创建 KafkaApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class KafkaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KafkaApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 KafkaApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
8.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/kafka 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Producer 的 Span 明细。如下图所示:
5、再之后,点击蓝圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Consumer 的 Span 明细。如下图所示:
9. RabbitMQ 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-rabbitmq。
本小节,我们来搭建一个 Zipkin 对 RabbitMQ 消息的发送和消费的链路追踪。该链路通过如下插件实现收集:
我们将使用 Spring-AMQP 进行 RabbitMQ 的操作。对 RabbitMQ 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《芋道 Spring Boot 消息队列 RabbitMQ 入门》文章。
考虑到让示例更简单,我们的示例项目包含 RabbitMQ 的生产者 Producer 和消费者 Consumer。
9.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-rabbitmq</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 RabbitMQ 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 RabbitMQ 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-rabbit</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-instrumentation-spring-rabbit依赖。
9.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 RabbitMQ 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-rabbitmq
# RabbitMQ 配置项,对应 RabbitProperties 配置类
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1 # RabbitMQ 服务的地址
port: 5672 # RabbitMQ 服务的端口
username: guest # RabbitMQ 服务的账号
password: guest # RabbitMQ 服务的密码9.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,额外增加了如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
// ==================== RabbitMQ 相关 ====================
@Bean
public SpringRabbitTracing springRabbitTracing(Tracing tracing) {
return SpringRabbitTracing.newBuilder(tracing)
.remoteServiceName("demo-mq-rabbit") // 远程 RabbitMQ 服务名,可自定义
.build();
}
@Bean
public BeanPostProcessor rabbitmqBeanPostProcessor(SpringRabbitTracing springRabbitTracing) {
return new BeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 如果是 RabbitTemplate ,针对 RabbitMQ Producer
if (bean instanceof RabbitTemplate) {
return springRabbitTracing.decorateRabbitTemplate((RabbitTemplate) bean);
}
// 如果是 SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory ,针对 RabbitMQ Consumer
if (bean instanceof SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory) {
return springRabbitTracing.decorateSimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory((SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory) bean);
}
return bean;
}
};
}#springRabbitTracing(...)方法,创建 SpringRabbitTracing Bean。#rabbitmqBeanPostProcessor(...)方法,自定义 BeanPostProcessor 处理器,将 RabbitTemplate 和 SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory Bean 进行装饰,实现对 RabbitMQ Producer 发送消息和 Consumer 消费消息的链路追踪。- 另外,如果胖友有采集率的需求,可以看看《brave-instrumentation-spring-rabbit ------ Sampling Policy》文档。
另外,在 RabbitConfig 配置类中,我们配合了 RabbitMQ Queue、Exchange、Binding。代码如下:
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
// 创建 Queue
@Bean
public Queue demoQueue() {
return new Queue(DemoMessage.QUEUE, // Queue 名字
true, // durable: 是否持久化
false, // exclusive: 是否排它
false); // autoDelete: 是否自动删除
}
// 创建 Direct Exchange
@Bean
public DirectExchange demoExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(DemoMessage.EXCHANGE,
true, // durable: 是否持久化
false); // exclusive: 是否排它
}
// 创建 Binding
// Exchange:DemoMessage.EXCHANGE
// Routing key:DemoMessage.ROUTING_KEY
// Queue:DemoMessage.QUEUE
@Bean
public Binding demoBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(demoQueue()).to(demoExchange()).with(DemoMessage.ROUTING_KEY);
}
}9.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private DemoProducer producer;
@GetMapping("/rabbitmq")
public String echo() {
this.sendMessage(1);
return "rabbitmq";
}
public void sendMessage(Integer id) {
producer.syncSend(id);
}
}- 在
/demo/rabbitmq接口中,会执行一次 RabbitMQ 发送消息的操作。 - DemoMessage 消息类,直接点击查看。
- DemoProducer 生产者类,直接点击查看。
- DemoConsumer 消费者类,直接点击查看。
9.5 RabbitMQApplication
创建 RabbitMQApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class RabbitMQApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RabbitMQApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 RabbitMQApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
9.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/rabbitmq 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Producer 的 Span 明细。如下图所示: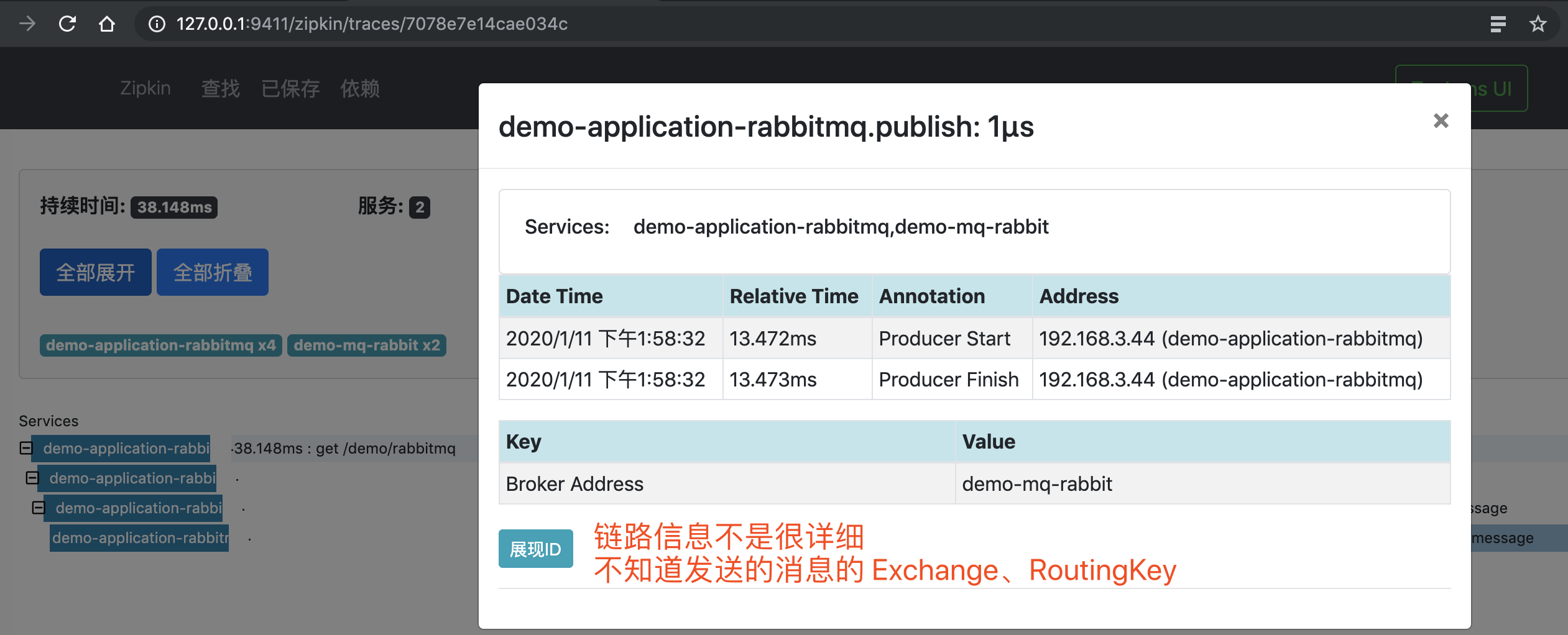
5、再之后,点击蓝圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Consumer 的 Span 明细。如下图所示:
10. ActiveMQ 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-activemq。
本小节,我们来搭建一个 Zipkin 对 ActiveMQ 消息的发送和消费的链路追踪。该链路通过如下插件实现收集:
ActiveMQ Java 客户端,基于 JMS 1.1 规范实现。
我们将使用 Spring-JMS 进行 ActiveMQ 的操作。对 ActiveMQ 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《Spring Boot 消息队列 ActiveMQ 入门》文章。
考虑到让示例更简单,我们的示例项目包含 ActiveMQ 的生产者 Producer 和消费者 Consumer。
10.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-activemq</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 ActiveMQ 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 JMS 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-jms</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-instrumentation-jms依赖。
10.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 ActiveMQ 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-activemq
# ActiveMQ 配置项,对应 ActiveMQProperties 配置类
activemq:
broker-url: tcp://127.0.0.1:61616 # Activemq Broker 的地址
user: admin # 账号
password: admin # 密码
packages:
trust-all: true # 可信任的反序列化包10.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,额外增加了如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
// ==================== ActiveMQ 相关 ====================
@Bean
public JmsTracing jmsTracing(Tracing tracing) {
return JmsTracing.newBuilder(tracing)
.remoteServiceName("demo-mq-activemq") // 远程 ActiveMQ 服务名,可自定义
.build();
}
@Bean
public BeanPostProcessor activeMQBeanPostProcessor(JmsTracing jmsTracing) {
return new BeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 如果是 ConnectionFactory ,针对 ActiveMQ Producer 和 Consumer
if (bean instanceof ConnectionFactory) {
return jmsTracing.connectionFactory((ConnectionFactory) bean);
}
return bean;
}
};
}#jmsTracing(...)方法,创建 JmsTracing Bean。#activeMQBeanPostProcessor(...)方法,自定义 BeanPostProcessor 处理器,将 ConnectionFactory 进行装饰,实现对 ActiveMQ Producer 发送消息和 Consumer 消费消息的链路追踪。- 另外,如果胖友有采集率的需求,可以看看《Brave JMS instrumentation ------ Sampling Policy》文档。
10.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private DemoProducer producer;
@GetMapping("/activemq")
public String echo() {
this.sendMessage(1);
return "activemq";
}
public void sendMessage(Integer id) {
producer.syncSend(id);
}
}- 在
/demo/activemq接口中,会执行一次 ActiveMQ 发送消息的操作。 - DemoMessage 消息类,直接点击查看。
- DemoProducer 生产者类,直接点击查看。
- DemoConsumer 消费者类,直接点击查看。
10.5 ActiveMQApplication
创建 ActiveMQApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class ActiveMQApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ActiveMQApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 ActiveMQApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。
10.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/rabbitmq 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Producer 的 Span 明细。如下图所示:
5、再之后,点击蓝圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Consumer 的 Span 明细。如下图所示: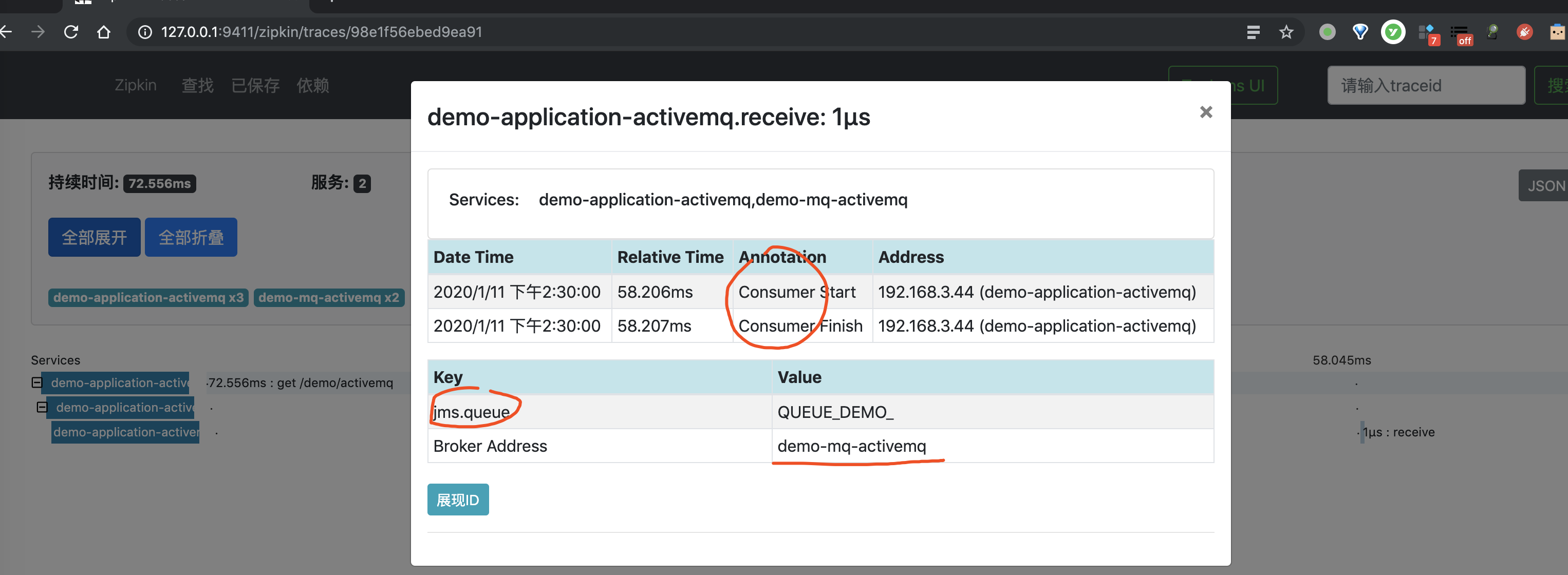
11. 日志框架示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-logback。
在使用 Zipkin 排查问题的时候,我们可能希望能够跟链路的日志进行关联,那么我们可以将链路编号( Zipkin TraceId )记录到日志中,从而进行关联。
友情提示:艿艿自己的项目里,在一些业务数据希望跟 Zipkin 链路进行关联时,会考虑新增一个
traceId字段,存储 Zipkin TraceId。例如说:
- 发送聊天消息时,消息记录上会存储链路编号。
- 创建交易订单时,订单记录上会存储链路编号。
这样,在排查该数据记录时,我们就可以拿着
traceId字段,去查响应的链路信息和日志信息。
Brave 提供了多种日志框架的支持,通过不同的插件:
本小节,我们来搭建一个 SLF4J + Logback 日志的 Zipkin TraceId 的集成示例。对 Logging 感兴趣的胖友,可以后续去看看《Spring Boot 日志框架 Logging 入门》文章。
11.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-logback</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Integrates so you can use log patterns like %X{traceId}/%X{spanId} -->
<!-- Brave 对 SLF4J 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-context-slf4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-context-slf4j依赖。
11.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 MongoDB 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-springmvc
logging:
pattern:
console: "%clr(%d{${LOG_DATEFORMAT_PATTERN:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}}){faint} %clr(${LOG_LEVEL_PATTERN:-%5p}) %clr(${PID:- }){magenta} %X{traceId}/%X{spanId} %clr(---){faint} %clr([%15.15t]){faint} %clr(%-40.40logger{39}){cyan} %clr(:){faint} %m%n${LOG_EXCEPTION_CONVERSION_WORD:%wEx}"
file: "%d{${LOG_DATEFORMAT_PATTERN:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}} ${LOG_LEVEL_PATTERN:-%5p} ${PID:- } %X{traceId}/%X{spanId} --- [%t] %-40.40logger{39} : %m%n${LOG_EXCEPTION_CONVERSION_WORD:%wEx}"日志配置有点长哈,主要配置 2 处地方 ,我们来看看图。如下图锁标记:
%X{traceId}:链路 Trace Id%X{spanId}:链路 Span Id
11.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,修改如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
@Bean
public Tracing tracing(@Value("${spring.application.name}") String serviceName) {
return Tracing.newBuilder()
.localServiceName(serviceName)
.currentTraceContext(ThreadLocalCurrentTraceContext.newBuilder()
.addScopeDecorator(MDCScopeDecorator.create()) // puts trace IDs into logs
.build()
)
.spanReporter(spanReporter()).build();
}- 通过
#currentTraceContext(CurrentTraceContext currentTraceContext)方法,设置链路 traceId 和 spanId 到 ThreadLocal 中,最终通过 SLF4J MDC 机制,设置到日志中。
11.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@GetMapping("/logback")
public String echo() {
logger.info("测试日志");
return "logback";
}
}- 在
/demo/logback接口中,会执行一次日志的记录。
11.5 LogbackApplication
创建 LogbackApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class LogbackApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ActiveMQApplication.class, args);
}
}执行 LogbackApplication,启动该 Spring Boot 应用。启动日志如下:
// ... 省略其它日志
2020-01-08 20:07:58.769 - INFO 69220 / --- [ main] c.i.s.l.zipkindemo.LogbackApplication : Started LogbackApplication in 2.491 seconds (JVM running for 3.254)- 因为此时没有链路的 TraceId 和 SpanId,所以
%X{traceId}/%X{spanId}占位符被替换成了/。
11.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/logback 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。看到日志如下:
2020-01-08 20:09:47.466 - INFO 69220 964658aaca06b156/964658aaca06b156 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] c.i.s.l.z.controller.DemoController : 测试日志%X{traceId}/%X{spanId}占位符被替换成了964658aaca06b156/964658aaca06b156。因为这里只有一个 Span,所以 TraceId 和 SpanId 相同。
2、然后,可以使用该 Zipkin TraceId 在 Zipkin UI 中,进行检索。如下图所示:
12. OpenTracing 示例
示例代码对应仓库:lab-40-opentracing。
在开始本节之前,推荐胖友先阅读下《OpenTracing 官方标准 ------ 中文版》规范,对 OpenTracing 有个简单的了解。
在 opentracing-java 项目中,定义了 OpenTracing Java API。而 brave-opentracing 项目,提供了对该 OpenTracing Java API 的实现。这样,我们就可以将使用 OpenTracing API 收集的链路数据,发送给 Zipkin Server 中。
下面,我们来搭建一个 OpenTracing Java API 的使用示例。
12.1 引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-opentracing</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Adds the MVC class and method names to server spans -->
<!-- Brave 对 Spring MVC 的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-spring-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 对 Opentracing 的实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.opentracing.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-opentracing</artifactId>
<version>0.35.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 SpringMVC 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-opentracing依赖。
14.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: demo-application-opentracing14.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」整体 一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。不过在 ZipkinConfiguration 中,额外增加了如下 Bean 的配置。代码如下:
// ZipkinConfiguration.java
// ==================== 通用配置 ====================
@Bean
public Tracer openTracer(Tracing tracing) {
return BraveTracer.create(tracing);
}#openTracer()方法,创建一个 BraveTracer Bean 对象。BraveTracer 是 Opentracing Tracer 接口的实现类。
14.4 DemoController
在 cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.controller 包路径下,创建 DemoController 类,提供示例 API 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private Tracer tracer;
@GetMapping("/opentracing")
public String echo() {
// 创建一个 Span
tracer.buildSpan("custom_operation").withTag("mp", "芋道源码").start().finish();
// 返回
return "opentracing";
}
}- 在
/demo/opentracing接口中的<X>处,我们使用 Opentracing Java API 创建了一个 Span。 - 更多的 Opentracing Java API 的使用,可以看看 opentracing-java 项目提供的示例哈。
14.4 OpentracingApplication
创建 OpentracingApplication.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class OpentracingApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OpentracingApplication.class, args);
}
}14.6 简单测试
1、首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/demo/opentracing 命令,请求下 Spring Boot 应用提供的 API。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
2、然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
3、之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示:
4、再之后,点击红圈 的个 Span,可以看到一个 Span 明细。如下图所示: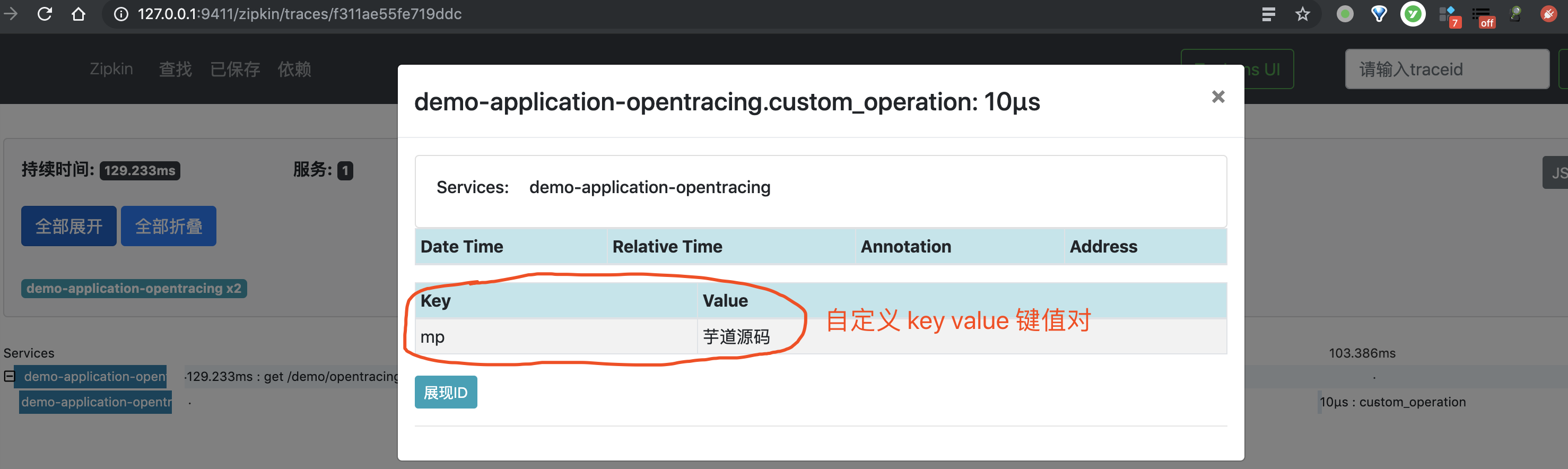
13. Dubbo 示例
示例代码对应仓库:
- 服务 API 项目:
lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-api- 服务 Provider 项目:
lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-provider- 服务 Consumer 项目:
lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-consumer
本小节,我们来搭建一个 Zipkin 对 Dubbo 的远程 RPC 调用的链路追踪。该链路通过如下插件实现收集:
友情提示:Brave 一共提供了两个插件,其中本文使用的
brave-instrumentation-dubbo适用于 Dubbo 2.7.X 版本,而另外的brave-instrumentation-dubbo-rpc适用于 Dubbo 2.6.X 版本。
我们来新建一个 lab-40-zipkin-dubbo 模块,一共包含三个子项目。最终如下图所示:
另外,考虑到目前 Dubbo 主要使用 Zookeeper 作为注册中心,所以本小节也是使用 Zookeeper。不了解的胖友,后续可以看看《Zookeeper 极简入门》文章。
13.1 搭建 API 项目
创建 lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-api 项目,服务接口,定义 Dubbo Service API 接口,提供给消费者使用。
13.1.1 UserService
创建 UserService 接口,定义用户服务 RPC Service 接口。代码如下:
public interface UserService {
/**
* 根据指定用户编号,获得用户信息
*
* @param id 用户编号
* @return 用户信息
*/
String get(Integer id);
}13.2 搭建服务提供者
创建 lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-provider 项目,服务提供者 ,实现 lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-api 项目定义的 Dubbo Service API 接口,提供相应的服务。
13.2.1 引入依赖
创建 pom.xml 文件中,引入依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-provider</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<!-- 引入定义的 Dubbo API 接口 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.iocoder.springboot.labs</groupId>
<artifactId>lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入 Spring Boot 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 实现对 Dubbo 的自动化配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用 Zookeeper 作为注册中心 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 核心库 -->
<!-- The below are needed to report traces to http://localhost:9411/api/v2/spans -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.reporter2</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-sender-okhttp3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Brave 针对 Dubbo 的插件,实现链路追踪 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-instrumentation-dubbo</artifactId>
<version>5.10.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<!-- Brave Bom 文件 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.brave</groupId>
<artifactId>brave-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.9.1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>- 相比「2.1 引入依赖」小节,主要 额外引入了
brave-instrumentation-dubbo依赖。
13.2.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Dubbo 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: user-service-provider
# dubbo 配置项,对应 DubboConfigurationProperties 配置类
dubbo:
# Dubbo 应用配置
application:
name: ${spring.application.name} # 应用名
# Dubbo 注册中心配
registry:
address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 # 注册中心地址。个鞥多注册中心,可见 http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/references/registry/introduction.html 文档。
# Dubbo 服务提供者协议配置
protocol:
port: -1 # 协议端口。使用 -1 表示随机端口。
name: dubbo # 使用 `dubbo://` 协议。更多协议,可见 http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/references/protocol/introduction.html 文档
# 配置扫描 Dubbo 自定义的 @Service 注解,暴露成 Dubbo 服务提供者
scan:
base-packages: cn.iocoder.springboot.lab40.zipkindemo.providerdemo.service
# Dubbo 服务提供者的配置,对应 ProviderConfig 类
provider:
filter: tracing重点是设置 dubbo.provider.filter 配置项为 tracing,使用 brave-instrumentation-dubbo 提供的 TracingFilter 过滤器,实现对 Dubbo 的链路追踪。不过实际上,TracingFilter 已经通过 @Activate 注解进行默认激活,所以也是可以不进行配置的。
关于
dubbo配置项,胖友可以后续阅读《Spring Boot Dubbo 入门》文章。
13.2.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 配置类。
13.2.4 UserServiceImpl
创建 UserServiceImpl 类,实现 UserService 接口,用户服务具体实现类。代码如下:
@org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Service(version = "1.0.0")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public String get(Integer id) {
return "user:" + id;
}
}13.2.5 ProviderApplication
创建 ProviderApplication 类,服务提供者的启动类。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class);
}
}13.3 搭建服务消费者
创建 lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-consumer 项目,服务消费者 ,会调用 lab-40-zipkin-dubbo-provider 项目提供的 User Service 服务。
13.3.1 引入依赖
创建 pom.xml 文件中,引入依赖。和「13.2.1 引入依赖」基本是一致的,胖友可以点击 pom.xml 文件查看。
13.3.2 配置文件
在 application.yml 中,添加 Dubbo 配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: user-service-consumer
# dubbo 配置项,对应 DubboConfigurationProperties 配置类
dubbo:
# Dubbo 应用配置
application:
name: ${spring.application.name} # 应用名
# Dubbo 注册中心配置
registry:
address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 # 注册中心地址。个鞥多注册中心,可见 http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/references/registry/introduction.html 文档。
# Dubbo 服务提供者的配置,对应 ConsumerConfig 类
consumer:
filter: tracing重点是设置 dubbo.consumer.filter 配置项为 tracing,使用 brave-instrumentation-dubbo 提供的 TracingFilter 过滤器,实现对 Dubbo 的链路追踪。不过实际上,TracingFilter 已经通过 @Activate 注解进行默认激活,所以也是可以不进行配置的。
关于
dubbo配置项,胖友可以后续阅读《Spring Boot Dubbo 入门》文章。
13.3.3 配置类
和「2.3 配置类」一致,即 ZipkinConfiguration 和 SpringMvcConfiguration 配置类。
13.3.4 UserController
创建 UserController 类,提供调用 UserService 服务的 HTTP 接口。代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Reference(protocol = "dubbo", version = "1.0.0")
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/get")
public String get(@RequestParam("id") Integer id) {
return userService.get(id);
}
}13.3.5 ConsumerApplication
创建 ConsumerApplication 类,服务消费者的启动类。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class);
}
}13.4 简单测试
使用 ProviderApplication 启动服务提供者,使用 ConsumerApplication 启动服务消费者。
① 首先,使用 curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/get?id=1 命令,使用 Dubbo 调用 user-service 服务。因为,我们要追踪下该链路。
② 然后,继续使用浏览器,打开 http://127.0.0.1:9411/ 地址,查看链路数据。点击「查找」按钮,便可看到刚才我们调用接口的链路数据。如下图所示:
一条链路经过 user-service-consumer 和 user-service-provider 两个服务,一共有三个 Span。
③ 之后,我们点击该链路数据,可以看到一个 Trace 明细。如下图所示: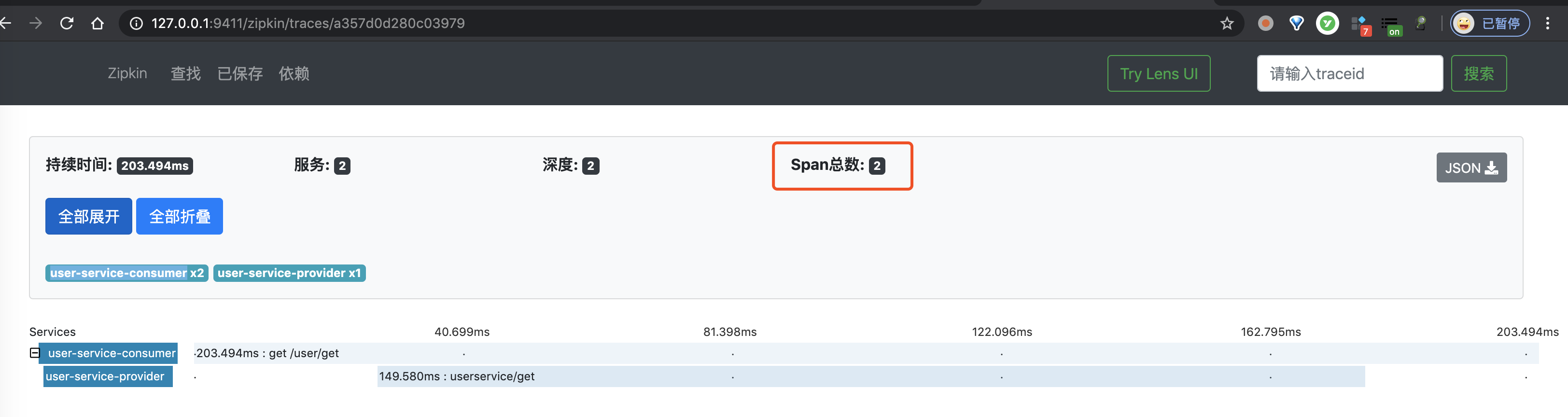
比较奇怪的是,此时我们两个 Span ,少了一个 Span !不晓得是不是 Zipkin UI 的 Bug?此时如果我们点击右上角的「JSON」按钮,查看该链路的原始数据,返回 JSON 如下图所示:
④ 再之后,分别点击个 Span,可以看到两个 Span 明细。如下图所示:
如果我们想要查找插件,可以按照如下的顺序:
- 一般情况下,我们可以优先去 brave 项目下,看看 Brave 是否有提供插件。
- 如果没有,则可以去 opentracing-contrib 项目下,看看 Opentracing 是否有提供插件。
- 如果还是没有,可以翻一翻使用的框架是否默认集成了 Opentracing 。
- 咳咳咳,再没有,那就自己写下吧,也不是非复杂,嘿嘿。
嘻嘻,想要对 Zipkin 做进一步深入的胖友,欢迎来看《Zipkin 源码解析》。美滋滋~
另外,有一个开源项目 https://github.com/opentracing-contrib/java-agent/,提供了基于 Java Agent 的 OpenTracing 增强,感兴趣的胖友,后续也可以研究一波。不过,这个项目貌似不太更新了。
不过从个人选择的角度的话,我还是选择使用 SkyWalking 作为链路追踪组件。功能更强大,插件更完善。感兴趣的胖友,可以看看《Spring Boot 链路追踪 SkyWalking 入门》文章。
当然,技术选型是个多选题,建议都去尝试下,才能更有体会,胖友你说是不?!
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42073629/article/details/106796176